Structural basis of membrane invagination by F-BAR domains
- PMID: 18329367
- PMCID: PMC2384079
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.041
Structural basis of membrane invagination by F-BAR domains
Abstract
BAR superfamily domains shape membranes through poorly understood mechanisms. We solved structures of F-BAR modules bound to flat and curved bilayers using electron (cryo)microscopy. We show that membrane tubules form when F-BARs polymerize into helical coats that are held together by lateral and tip-to-tip interactions. On gel-state membranes or after mutation of residues along the lateral interaction surface, F-BARs adsorb onto bilayers via surfaces other than their concave face. We conclude that membrane binding is separable from membrane bending, and that imposition of the module's concave surface forces fluid-phase bilayers to bend locally. Furthermore, exposure of the domain's lateral interaction surface through a change in orientation serves as the crucial trigger for assembly of the helical coat and propagation of bilayer bending. The geometric constraints and sequential assembly of the helical lattice explain how F-BAR and classical BAR domains segregate into distinct microdomains, and provide insight into the spatial regulation of membrane invagination.
Figures

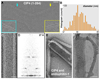
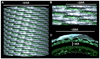
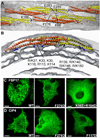

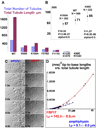

Comment in
-
Flexible scaffolding made of rigid BARs.Cell. 2008 Mar 7;132(5):727-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.025. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18329357
References
-
- Brett TJ, Traub LM. Molecular structures of coat and coat-associated proteins: function follows form. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:395–406. - PubMed
-
- Bruinsma R, Pincus P. Protein aggregation in membranes. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science. 1996;1:401–406.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 RR17573/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32GM07205/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR017573/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA018343/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DK45735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA46128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007205/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB001567/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NCRR 19895-02/PHS HHS/United States
- R21 DA024101/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA046128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM071590/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071590/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DA024101/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EB001567/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

