Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters
- PMID: 18329372
- PMCID: PMC2323338
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.019
Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters
Abstract
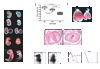
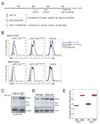
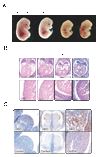
miR-17 approximately 92, miR-106b approximately 25, and miR-106a approximately 363 belong to a family of highly conserved miRNA clusters. Amplification and overexpression of miR-1792 is observed in human cancers, and its oncogenic properties have been confirmed in a mouse model of B cell lymphoma. Here we show that mice deficient for miR-17 approximately 92 die shortly after birth with lung hypoplasia and a ventricular septal defect. The miR-17 approximately 92 cluster is also essential for B cell development. Absence of miR-17 approximately 92 leads to increased levels of the proapoptotic protein Bim and inhibits B cell development at the pro-B to pre-B transition. Furthermore, while ablation of miR-106b approximately 25 or miR-106a approximately 363 has no obvious phenotypic consequences, compound mutant embryos lacking both miR-106b approximately 25 and miR-17 approximately 92 die at midgestation. These results provide key insights into the physiologic functions of this family of microRNAs and suggest a link between the oncogenic properties of miR-17 approximately 92 and its functions during B lymphopoiesis and lung development.
Figures




Comment in
-
MicroRNAs and lymphocyte homeostasis: dangerous eggs in a single basket.Immunol Cell Biol. 2008 Jul;86(5):387-8. doi: 10.1038/icb.2008.33. Epub 2008 May 20. Immunol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18490933 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bagga S, Bracht J, Hunter S, Massirer K, Holtz J, Eachus R, Pasquinelli AE. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP, Chen CZ. Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:396–400. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA, Murchison EP, Alcorn H, Li MZ, Mills AA, Elledge SJ, Anderson KV, Hannon GJ. Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet. 2003;35:215–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

