One-step affinity tag purification of full-length recombinant human AP-1 complexes from bacterial inclusion bodies using a polycistronic expression system
- PMID: 18329890
- PMCID: PMC2354920
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2008.01.016
One-step affinity tag purification of full-length recombinant human AP-1 complexes from bacterial inclusion bodies using a polycistronic expression system
Abstract
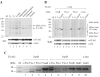
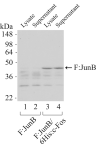
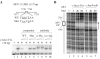
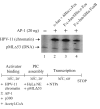
The AP-1 transcription factor is a dimeric protein complex formed primarily between Jun (c-Jun, JunB, JunD) and Fos (c-Fos, FosB, Fra-1, Fra-2) family members. These distinct AP-1 complexes are expressed in many cell types and modulate target gene expression implicated in cell proliferation, differentiation, and stress responses. Although the importance of AP-1 has long been recognized, the biochemical characterization of AP-1 remains limited in part due to the difficulty in purifying full-length, reconstituted dimers with active DNA-binding and transcriptional activity. Using a combination of bacterial coexpression and epitope-tagging methods, we successfully purified all 12 heterodimers (3 Junx4 Fos) of full-length human AP-1 complexes as well as c-Jun/c-Jun, JunD/JunD, and c-Jun/JunD dimers from bacterial inclusion bodies using one-step nickel-NTA affinity tag purification following denaturation and renaturation of coexpressed AP-1 subunits. Coexpression of two constitutive components in a dimeric AP-1 complex helps stabilize the proteins when compared with individual protein expression in bacteria. Purified dimeric AP-1 complexes are functional in sequence-specific DNA binding, as illustrated by electrophoretic mobility shift assays and DNase I footprinting, and are also active in transcription with in vitro-reconstituted human papillomavirus (HPV) chromatin containing AP-1-binding sites in the native configuration of HPV nucleosomes. The availability of these recombinant full-length human AP-1 complexes has greatly facilitated mechanistic studies of AP-1-regulated gene transcription in many biological systems.
Figures
References
-
- Eckert RL, Crish JF, Banks EB, Welter JF. The epidermis: genes on - genes off. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1997;109:501–509. - PubMed
-
- Shaulian E, Karin M. AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:E131–136. - PubMed
-
- Eferl R, Wagner EF. AP-1: a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2003;3:859–868. - PubMed
-
- Angel P, Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1991;1072:129–157. - PubMed
-
- Gentz R, Rauscher FJ, Abate C, Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989;243:1695–1699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

