An evolutionarily conserved cyclin homolog from Drosophila rescues yeast deficient in G1 cyclins
- PMID: 1833067
- PMCID: PMC2753436
- DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90043-x
An evolutionarily conserved cyclin homolog from Drosophila rescues yeast deficient in G1 cyclins
Abstract
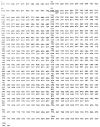
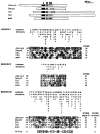
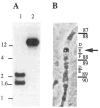
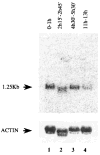
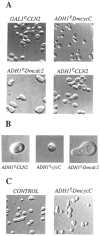
We have isolated two Drosophila cDNA clones that rescue Saccharomyces cerevisiae deficient in CLN functions. One of these clones is the Drosophila homolog of the cdc2 gene. The second encodes a distant and new member of the cyclin family of proteins, cyclin C. It is highly homologous (72% identity) to a human clone isolated in a similar screen. Yeast cells rescued by a plasmid constitutively expressing this Drosophila cyclin C are unusually small, consistent with an unregulated high level of G1 cyclin function. Sequence comparisons identified regions conserved among the more distantly related cyclins. Based on these conserved elements, we identified homology between cyclins and the ras oncogene.
Figures
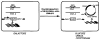

References
-
- Burgers PM, Percival KJ. Transformation of yeast spheroplasts without cell fusion. Anal Biochem. 1987;163:391–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

