Clinical investigation in highly disease-affected rheumatoid arthritis patients in Japan with adalimumab applying standard and general evaluation: the CHANGE study
- PMID: 18330677
- PMCID: PMC2668560
- DOI: 10.1007/s10165-008-0045-0
Clinical investigation in highly disease-affected rheumatoid arthritis patients in Japan with adalimumab applying standard and general evaluation: the CHANGE study
Abstract
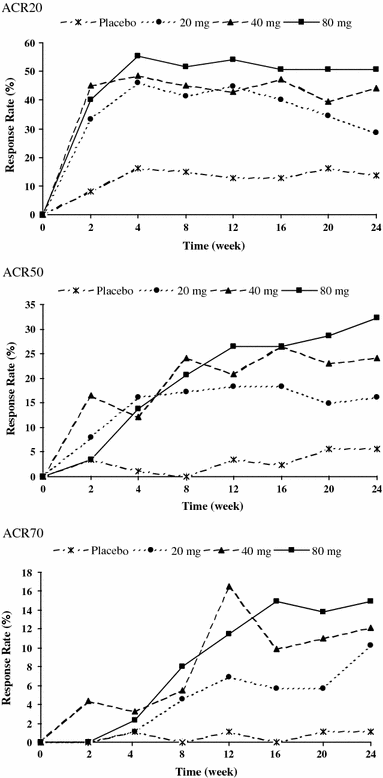
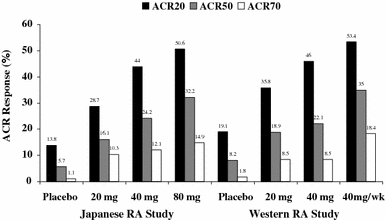
This multicenter, double-blind study evaluated the effects of three doses of adalimumab in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Patients were randomized to placebo (n = 87) or adalimumab 20 mg (n = 87), 40 mg (n = 91), or 80 mg (n = 87) every other week for 24 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was the American College of Rheumatology criteria for 20% improvement (ACR20) at Week 24. At Week 24, all adalimumab treatment groups achieved statistically significantly better ACR20 response rates (20 mg: 28.7%, P < 0.05; 40 mg: 44.0%, P < 0.001; and 80 mg: 50.6%, P < 0.001) versus placebo (13.8%), as well as statistically significantly greater ACR50 and ACR70 responses for the two higher adalimumab doses versus placebo. Rates of adverse events were comparable between the adalimumab groups and the placebo group, except for injection-site reactions, which occurred in more adalimumab-treated patients. Adalimumab 20, 40, and 80 mg were safe and effective in Japanese patients; however, the greatest responses occurred with the 40 and 80 mg doses. These results and comparable ACR20 responses in Western patients support adalimumab 40 mg every other week as the appropriate dosage to treat RA in Japanese patients.
Figures

References
-
- Kvien TK. Epidemiology and burden of illness of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(Suppl 1):1–12. - PubMed
-
- Shiokawa Y. International conference for the bone and joint decade. Rheumatic diseases at the dawn of the millennium. J Rheumatol. 2003;30(Suppl 67):1–2. - PubMed
-
- Mugitani M. International conference for the bone and joint decade. Bone and joint diseases around the world. Japan: strategy for rheumatic disease control. J Rheumatol. 2003;30(Suppl 67):47.

