Staging accuracy of esophageal cancer by endoscopic ultrasound: a meta-analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 18330935
- PMCID: PMC2693739
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.1479
Staging accuracy of esophageal cancer by endoscopic ultrasound: a meta-analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) in the staging of esophageal cancer.
Methods: Only EUS studies confirmed by surgery were selected. Articles were searched in Medline and Pubmed. Two reviewers independently searched and extracted data. Meta-analysis of the accuracy of EUS was analyzed by calculating pooled estimates of sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios, and diagnostic odds ratio. Pooling was conducted by both the Mantel-Haenszel method (fixed effects model) and DerSimonian Laird method (random effects model). The heterogeneity of studies was tested using Cochran's Q test based upon inverse variance weights.
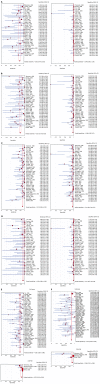
Results: Forty-nine studies (n = 2558) which met the inclusion criteria were included in this analysis. Pooled sensitivity and specificity of EUS to diagnose T1 was 81.6% (95% CI: 77.8-84.9) and 99.4% (95% CI: 99.0-99.7), respectively. To diagnose T4, EUS had a pooled sensitivity of 92.4% (95% CI: 89.2-95.0) and specificity of 97.4% (95% CI: 96.6-98.0). With Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA), sensitivity of EUS to diagnose N stage improved from 84.7% (95% CI: 82.9-86.4) to 96.7% (95% CI: 92.4-98.9). The P value for the c2 test of heterogeneity for all pooled estimates was > 0.10.
Conclusion: EUS has excellent sensitivity and specificity in accurately diagnosing the TN stage of esophageal cancer. EUS performs better with advanced (T4) than early (T1) disease. FNA substantially improves the sensitivity and specificity of EUS in evaluating N stage disease. EUS should be strongly considered for staging esophageal cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Cossentino MJ, Wong RK. Barrett's esophagus and risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Semin Gastrointest Dis. 2003;14:128–135. - PubMed
-
- Bollschweiler E, Wolfgarten E, Gutschow C, Holscher AH. Demographic variations in the rising incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma in white males. Cancer. 2001;92:549–555. - PubMed
-
- Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK. The changing epidemiology of esophageal cancer. Semin Oncol. 1999;26:2–8. - PubMed
-
- Holmes RS, Vaughan TL. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of esophageal cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17:2–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

