sSgo1, a major splice variant of Sgo1, functions in centriole cohesion where it is regulated by Plk1
- PMID: 18331714
- PMCID: PMC2279080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.12.007
sSgo1, a major splice variant of Sgo1, functions in centriole cohesion where it is regulated by Plk1
Abstract
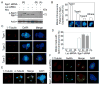
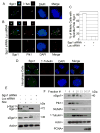
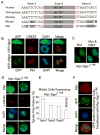
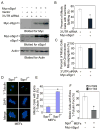
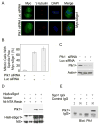
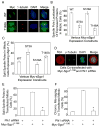
Shugoshin 1 (Sgo1) functions as a protector of centromeric cohesion of sister chromatids in higher eukaryotes. Here, we provide evidence for a previously unrecognized role for Sgo1 in centriole cohesion. Sgo1 depletion via RNA interference induces the formation of multiple centrosome-like structures in mitotic cells that result from the separation of paired centrioles. Sgo1+/- mitotic murine embryonic fibroblasts display split centrosomes. Localization study of two major endogenous splice variants of Sgo1 indicates that the smaller variant, sSgo1, is found at the centrosome in interphase and at spindle poles in mitosis. sSgo1 interacts with Plk1 and its spindle pole localization is Plk1 dependent. Centriole splitting induced by Sgo1 depletion or expression of a dominant negative mutant is suppressed by ectopic expression of sSgo1 or by Plk1 knockdown. Our studies strongly suggest that sSgo1 plays an essential role in protecting centriole cohesion, which is partly regulated by Plk1.
Figures

Comment in
-
sSgo1, a guardian of centriole cohesion.Dev Cell. 2008 Mar;14(3):320-2. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.02.008. Dev Cell. 2008. PMID: 18331711
References
-
- Arnaud L, Pines J, Nigg EA. GFP tagging reveals human Polo-like kinase 1 at the kinetochore/centromere region of mitotic chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1998;107:424–429. - PubMed
-
- Blomberg-Wirschell M, Doxsey SJ. Rapid isolation of centrosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1998;298:228–238. - PubMed
-
- Clarke AS, Tang TT, Ooi DL, Orr-Weaver TL. POLO kinase regulates the Drosophila centromere cohesion protein MEI-S332. Dev Cell. 2005;8:53–64. - PubMed
-
- Dionne MA, Howard L, Compton DA. NuMA is a component of an insoluble matrix at mitotic spindle poles. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1999;42:189–203. - PubMed
-
- Doxsey S, McCollum D, Theurkauf W. Centrosomes in cellular regulation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:411–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

