Central nervous system neuropeptide Y signaling modulates VLDL triglyceride secretion
- PMID: 18332095
- PMCID: PMC3968924
- DOI: 10.2337/db07-1702
Central nervous system neuropeptide Y signaling modulates VLDL triglyceride secretion
Abstract
Objective: Elevated triglyceride (TG) is the major plasma lipid abnormality in obese and diabetic patients and contributes to cardiovascular morbidity in these disorders. We sought to identify novel mechanisms leading to hypertriglyceridemia. Resistance to negative feedback signals from adipose tissue in key central nervous system (CNS) energy homeostatic circuits contributes to the development of obesity. Because triglycerides both represent the largest energy depot in the body and are elevated in both the plasma and adipose in obesity and diabetes, we hypothesized that the same neural circuits that regulate energy balance also regulate the secretion of TGs into plasma.
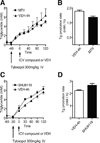
Research design and methods: In normal fasting rats, the TG secretion rate was estimated by serial blood sampling after intravascular tyloxapol pretreatment. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) signaling in the CNS was modulated by intracerebroventricular injection of NPY, receptor antagonist, and receptor agonist.
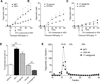
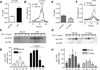
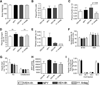
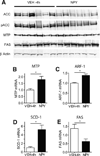
Results: A single intracerebroventricular injection of NPY increased TG secretion by 2.5-fold in the absence of food intake, and this was determined to be VLDL by fast performance liquid chromatography (FPLC). This effect was recapitulated by activating NPY signaling in downstream neurons with an NPY-Y5 receptor agonist. An NPY-Y1 receptor antagonist decreased the elevated TGs in the form of VLDL secretion rate by 50% compared with vehicle. Increased TG secretion was due to increased secretion of VLDL particles, rather than secretion of larger particles, because apolipoprotein B100 was elevated in FPLC fractions corresponding to VLDL.
Conclusions: We find that a key neuropeptide system involved in energy homeostasis in the CNS exerts control over VLDL-TG secretion into the bloodstream.
Figures
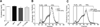
References
-
- Chahil TJ, Ginsberg HN. Diabetic dyslipidemia. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2006;35:491–510. vii–viii. - PubMed
-
- Castelli WP, Garrison RJ, Wilson PW, Abbott RD, Kalousdian S, Kannel WB. Incidence of coronary heart disease and lipoprotein cholesterol levels: The Framingham Study. JAMA. 1986;256:2835–2838. - PubMed
-
- Fuller JH, Stevens LK, Wang SL. Risk factors for cardiovascular mortality and morbidity: the WHO Mutinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001;44(Suppl. 2):S54–S64. - PubMed
-
- Elovson J, Chatterton JE, Bell GT, Schumaker VN, Reuben MA, Puppione DL, Reeve JR, Jr, Young NL. Plasma very low density lipoproteins contain a single molecule of apolipoprotein B. J Lipid Res. 1988;29:1461–1473. - PubMed
-
- Pullinger CR, North JD, Teng BB, Rifici VA, Ronhild de Brito AE, Scott J. The apolipoprotein B gene is constitutively expressed in HepG2 cells: regulation of secretion by oleic acid, albumin, and insulin, and measurement of the mRNA half-life. J Lipid Res. 1989;30:1065–1077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

