Transcription regulation of the rRNA gene by a multifunctional nucleolar protein, B23/nucleophosmin, through its histone chaperone activity
- PMID: 18332108
- PMCID: PMC2423177
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02078-07
Transcription regulation of the rRNA gene by a multifunctional nucleolar protein, B23/nucleophosmin, through its histone chaperone activity
Abstract
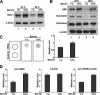
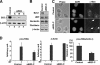
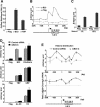
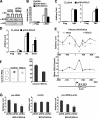
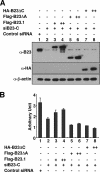
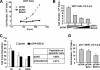
It is well established that the transcription rate of the rRNA gene is closely associated with profound alterations in the cell growth rate. Regulation of rRNA gene transcription is likely to be dependent on the dynamic conversion of the chromatin structure. Previously, we identified B23/nucleophosmin, a multifunctional nucleolar phosphoprotein, as a component of template activating factor III that remodels the chromatin-like structure of the adenovirus genome complexed with viral basic proteins. It has also been shown that B23 has histone chaperone activity. Here, we examined the effect of B23 on rRNA gene transcription. B23 was found to be associated with the rRNA gene chromatin. Small-interfering-RNA-mediated down-regulation of the B23 expression level resulted in reduction of the transcription rate of the rRNA gene. We constructed a B23 mutant termed B23DeltaC, which lacks the domain essential for the histone chaperone activity and inhibited the histone binding activity of B23 in a dominant-negative manner. Expression of B23DeltaC decreased rRNA gene transcription and the rate of cell proliferation. These results suggest that B23 is involved in the transcription regulation of the rRNA gene as a nucleolar histone chaperone.
Figures


References
-
- Chang, J. H., and M. O. Olson. 1990. Structure of the gene for rat nucleolar protein B23. J. Biol. Chem. 26518227-18233. - PubMed
-
- Colombo, E., J. C. Marine, D. Danovi, B. Falini, and P. G. Pelicci. 2002. Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat. Cell Biol. 4529-533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
