Abnormal sympathoadrenal development and systemic hypotension in PHD3-/- mice
- PMID: 18332118
- PMCID: PMC2423159
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02041-07
Abnormal sympathoadrenal development and systemic hypotension in PHD3-/- mice
Abstract
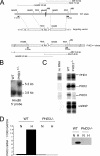
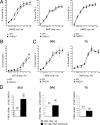
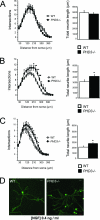
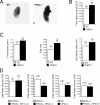
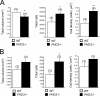
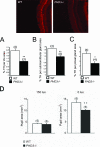
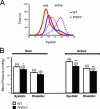
Cell culture studies have implicated the oxygen-sensitive hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase PHD3 in the regulation of neuronal apoptosis. To better understand this function in vivo, we have created PHD3(-/-) mice and analyzed the neuronal phenotype. Reduced apoptosis in superior cervical ganglion (SCG) neurons cultured from PHD3(-/-) mice is associated with an increase in the number of cells in the SCG, as well as in the adrenal medulla and carotid body. Genetic analysis by intercrossing PHD3(-/-) mice with HIF-1a(+/-) and HIF-2a(+/-) mice demonstrated an interaction with HIF-2alpha but not HIF-1alpha, supporting the nonredundant involvement of a PHD3-HIF-2alpha pathway in the regulation of sympathoadrenal development. Despite the increased number of cells, the sympathoadrenal system appeared hypofunctional in PHD3(-/-) mice, with reduced target tissue innervation, adrenal medullary secretory capacity, sympathoadrenal responses, and systemic blood pressure. These observations suggest that the role of PHD3 in sympathoadrenal development extends beyond simple control of cell survival and organ mass, with functional PHD3 being required for proper anatomical and physiological integrity of the system. Perturbation of this interface between developmental and adaptive signaling by hypoxic, metabolic, or other stresses could have important effects on key sympathoadrenal functions, such as blood pressure regulation.
Figures
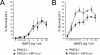
References
-
- Appelhoff, R. J., Y. M. Tian, R. R. Raval, H. Turley, A. L. Harris, C. W. Pugh, P. J. Ratcliffe, and J. M. Gleadle. 2004. Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J. Biol. Chem. 27938458-38465. - PubMed
-
- Aragones, J., M. Schneider, K. Van Geyte, P. Fraisl, T. Dresselaers, M. Mazzone, R. Dirkx, S. Zacchigna, H. Lemieux, N. H. Jeoung, D. Lambrechts, T. Bishop, P. Lafuste, A. Diez-Juan, S. K. Harten, P. Van Noten, K. De Bock, C. Willam, M. Tjwa, A. Grosfeld, R. Navet, L. Moons, T. Vandendriessche, C. Deroose, B. Wijeyekoon, J. Nuyts, B. Jordan, R. Silasi-Mansat, F. Lupu, M. Dewerchin, C. Pugh, P. Salmon, L. Mortelmans, B. Gallez, F. Gorus, J. Buyse, F. Sluse, R. A. Harris, E. Gnaiger, P. Hespel, P. Van Hecke, F. Schuit, P. Van Veldhoven, P. Ratcliffe, M. Baes, P. Maxwell, and P. Carmeliet. 2008. Deficiency or inhibition of oxygen sensor Phd1 induces hypoxia tolerance by reprogramming basal metabolism. Nat. Genet. 40170-180. - PubMed
-
- Barker, D. J. 2002. Fetal programming of coronary heart disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 13364-368. - PubMed
-
- Barker, D. J., S. P. Bagby, and M. A. Hanson. 2006. Mechanisms of disease: in utero programming in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2700-707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
