The gap gets bigger: changes in mortality and life expectancy, by education, 1981-2000
- PMID: 18332489
- PMCID: PMC2366041
- DOI: 10.1377/hlthaff.27.2.350
The gap gets bigger: changes in mortality and life expectancy, by education, 1981-2000
Abstract
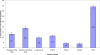
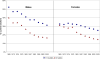
In this paper we examine educational disparities in mortality and life expectancy among non-Hispanic blacks and whites in the 1980s and 1990s. Despite increased attention and substantial dollars directed to groups with low socioeconomic status, within race and gender groups, the educational gap in life expectancy is rising, mainly because of rising differentials among the elderly. With the exception of black males, all recent gains in life expectancy at age twenty-five have occurred among better-educated groups, raising educational differentials in life expectancy by 30 percent. Differential trends in smoking-related diseases explain at least 20 percent of this trend.
Figures

References
-
- Kitagawa EM, Hauser PM. Differential Mortality in the United States: A Study in Socioeconomic Epidemiology. Harvard University Press; Cambridge, MA: 1973.
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services . In: Report of the Secretary's Task Force on Black & Minority Health. Health Status of Minorities and Low-Income Groups. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services., editor. Washington, D.C.: 1985. (Hyattsville, Maryland: 1985)
-
- Institute of Medicine . Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. In: Smedley BD, Stith AY, Nelson AR, editors. National Academies Press; 1−764. Washington, D.C.: 2003. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Healthy People 2010: Understanding and Improving Health (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 2000) - PubMed
-
- Healthcare Research and Quality Act of 1999. pp. 106–129.
-
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Medicaid Program - General Information, Technical Summary. 2005. [March 28, 2006]. http://www.cms.hhs.gov/MedicaidGenInfo/03_TechnicalSummary.asp.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

