Distal pancreatic resection: technical differences between open and laparoscopic approaches
- PMID: 18333239
- PMCID: PMC2131367
- DOI: 10.1080/13651820500468059
Distal pancreatic resection: technical differences between open and laparoscopic approaches
Abstract
Open distal pancreatic resection has been performed over the years for management of patients with a variety of pancreatic disorders. However, the technique is usually not performed in the same way by all surgeons. In recent years, the laparoscopic approach has been introduced with all the advantages of a minimally invasive procedure. The primary differences between the open and laparoscopic approaches are the method of access, the method of exposure, and the extent of operative trauma. The clinical advantages of the laparoscopic approach are the reduced length hospitalization, the reduction in postoperative pain, absence of wound-related complications and faster recovery.
Figures

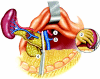



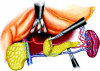
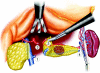
References
-
- Holdsworth RJ, Irving AD, Cuschieri A. Postsplenectomy sepsis and its mortality rate: actual versus perceived. Br J Surg. 1991;78:1031–8. - PubMed
-
- Kimura W, Inoue T, Futakawa N, Shinkai H, Muto T. Spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy with conservation of the splenic artery and vein. Surgery. 1996;120:885–90. - PubMed
-
- Warshaw AL. Conservation of the spleen with distal pancreatectomy. Arch Surg. 1988;123:550–3. - PubMed
-
- Aldridge MC, Williamson RCN. Distal pancreatectomy with and without splenectomy. Br J Surg. 1991;78:976–9. - PubMed
-
- Gagner M, Pomp A. Laparoscopic pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy. Surg Endosc. 1994;8:408–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

