C-terminal cleavage of the amyloid-beta protein precursor at Asp664: a switch associated with Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 18334752
- PMCID: PMC2818039
- DOI: 10.3233/jad-2008-13101
C-terminal cleavage of the amyloid-beta protein precursor at Asp664: a switch associated with Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
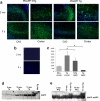
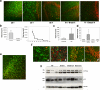
In addition to the proteolytic cleavages that give rise to amyloid-beta (Abeta), the amyloid-beta protein precursor (AbetaPP) is cleaved at Asp664 intracytoplasmically. This cleavage releases a cytotoxic peptide, APP-C31, removes AbetaPP-interaction motifs required for signaling and internalization, and is required for the generation of AD-like deficits in a mouse model of the disease. Although we and others had previously shown that Asp664 cleavage of AbetaPP is increased in AD brains, the distribution of the Asp664-cleaved forms of AbetaPP in non-diseased and AD brains at different ages had not been determined. Confirming previous reports, we found that Asp664-cleaved forms of AbetaPP were increased in neuronal cytoplasm and nuclei in early-stage AD brains but were absent in age-matched, non-diseased control brains and in late-stage AD brains. Remarkably, however, Asp664-cleaved AbetaPP was prominent in neuronal somata and in processes in entorhinal cortex and hippocampus of non-diseased human brains at ages <45 years. Our observations suggest that Asp664 cleavage of AbetaPP may be part of the normal proteolytic processing of AbetaPP in young (<45 years) human brain and that this cleavage is down-regulated with normal aging, but is aberrantly increased and altered in location in early AD.
Figures





References
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K, Fortini ME. Notch signaling. Science. 1995;268:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Baek SH, Ohgi KA, Rose DW, Koo EH, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. Exchange of N-CoR corepressor and Tip60 coactivator complexes links gene expression by NF-kappaB and beta-amyloid precursor protein. Cell. 2002;110:55–67. - PubMed
-
- Besnault-Mascard L, Leprince C, Auffredou MT, Meunier B, Bourgeade MF, Camonis J, Lorenzo HK, Vazquez A. Caspase-8 sumoylation is associated with nuclear localization. Oncogene. 2005;24:3268–3273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

