A new small molecule inhibitor of estrogen receptor alpha binding to estrogen response elements blocks estrogen-dependent growth of cancer cells
- PMID: 18337247
- PMCID: PMC2442351
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M709936200
A new small molecule inhibitor of estrogen receptor alpha binding to estrogen response elements blocks estrogen-dependent growth of cancer cells
Abstract
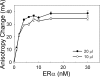
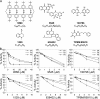
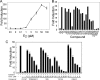
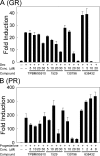
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) plays an important role in several human cancers. Most current ERalpha antagonists bind in the receptor ligand binding pocket and compete for binding with estrogenic ligands. Instead of the traditional approach of targeting estrogen binding to ER, we describe a strategy using a high throughput fluorescence anisotropy microplate assay to identify small molecule inhibitors of ERalpha binding to consensus estrogen response element (cERE) DNA. We identified small molecule inhibitors of ERalpha binding to the fluorescein-labeled (fl)cERE and evaluated their specificity, potency, and efficacy. One small molecule, theophylline, 8-[(benzylthio)methyl]-(7CI,8CI) (TPBM), inhibited ERalpha binding to the flcERE (IC(50) approximately 3 microm) and inhibited ERalpha-mediated transcription of a stably transfected ERE-containing reporter gene. Inhibition by TPBM was ER-specific, because progesterone and glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity were not significantly inhibited. In tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells that overexpress ERalpha, TPBM inhibited 17beta-estradiol (E(2))-ERalpha (IC(50) 9 microm) and 4-hydroxytamoxifen-ERalpha-mediated gene expression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation showed TPBM reduced E(2).ERalpha recruitment to an endogenous estrogen-responsive gene. TPBM inhibited E(2)-dependent growth of ERalpha-positive cancer cells (IC(50) of 5 microm). TPBM is not toxic to cells and does not affect estrogen-independent cell growth. TPBM acts outside of the ER ligand binding pocket, does not act by chelating the zinc in ER zinc fingers, and differs from known ERalpha inhibitors. Using a simple high throughput screen for inhibitors of ERalpha binding to the cERE, a small molecule inhibitor has been identified that selectively inhibits ERalpha-mediated gene expression and estrogen-dependent growth of cancer cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
PARP-1 as a novel target in endocrine-resistant breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 16;44(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03441-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40518539 Free PMC article.
-
Photochemical Metal-Free synthesis and biological Assessment of isocryptolepine analogues targeting estrogen receptor Alpha in breast cancer cells.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Dec;153:107942. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107942. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39515131
-
PFKFB3 regulates breast cancer tumorigenesis and Fulvestrant sensitivity by affecting ERα stability.Cell Signal. 2024 Jul;119:111184. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111184. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38640982
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) Estrogen Receptor Degraders for Treatment of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer.Target Oncol. 2025 May;20(3):431-444. doi: 10.1007/s11523-025-01137-5. Epub 2025 May 6. Target Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40327300 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A noncompetitive small molecule inhibitor of estrogen-regulated gene expression and breast cancer cell growth that enhances proteasome-dependent degradation of estrogen receptor {alpha}.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 31;285(53):41863-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.183723. Epub 2010 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 21041310 Free PMC article.
-
In search of novel drug target sites on estrogen receptors using RNA aptamers.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014 Jun;24(3):226-38. doi: 10.1089/nat.2013.0474. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014. PMID: 24588102 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput fluorescence anisotropy screen for inhibitors of the oncogenic mRNA binding protein, IMP-1.J Biomol Screen. 2014 Mar;19(3):427-36. doi: 10.1177/1087057113499633. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Biomol Screen. 2014. PMID: 24108120 Free PMC article.
-
Simple assay for screening phytoestrogenic compounds using the oestrogen receptor immobilised magnetite nanoparticles.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017 Jun;11(4):395-402. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2016.0139. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28530188 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic responses from the estrogen-responsive element-dependent signaling pathway mediated by estrogen receptor alpha are required to elicit cellular alterations.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 29;284(22):15277-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900365200. Epub 2009 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19321454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clarke, R., Liu, M. C., Bouker, K. B., Gu, Z., Lee, R. Y., Zhu, Y., Skaar, T. C., Gomez, B., O'Brien, K., Wang, Y., and Hilakivi-Clarke, L. A. (2003) Oncogene 22 7316–7339 - PubMed
-
- Jiang, X., Ellison, S. J., Alarid, E. T., and Shapiro, D. J. (2007) Oncogene 26 4106–4114 - PubMed
-
- Jiang, X., Orr, B. A., Kranz, D. M., and Shapiro, D. J. (2006) Endocrinology 147 1419–1426 - PubMed
-
- O'Lone, R., Frith, M. C., Karlsson, E. K., and Hansen, U. (2004) Mol. Endocrinol. 18 1859–1875 - PubMed
-
- Gradishar, W. J., and Cella, D. (2006) JAMA 295 2784–2786 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

