CAPON modulates cardiac repolarization via neuronal nitric oxide synthase signaling in the heart
- PMID: 18337493
- PMCID: PMC2393814
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0709118105
CAPON modulates cardiac repolarization via neuronal nitric oxide synthase signaling in the heart
Abstract
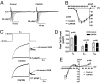
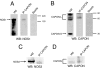
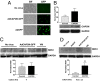
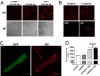
Congenital long- or short-QT syndrome may lead to life-threatening ventricular tachycardia and sudden cardiac death. Apart from the rare disease-causing mutations, common genetic variants in CAPON, a neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS1) regulator, have recently been associated with QT interval variations in a human whole-genome association study. CAPON had been unsuspected of playing a role in cardiac repolarization; indeed, its physiological role in the heart (if any) is unknown. To define the biological effects of CAPON in the heart, we investigated endogenous CAPON protein expression and protein-protein interactions in the heart and performed electrophysiological studies in isolated ventricular myocytes with and without CAPON overexpression. We find that CAPON protein is expressed in the heart and interacts with NOS1 to accelerate cardiac repolarization by inhibition of L-type calcium channel. Our findings provide a rationale for the association of CAPON gene variants with extremes of the QT interval in human populations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cardiac nitric oxide synthase-1 localization within the cardiomyocyte is accompanied by the adaptor protein, CAPON.Nitric Oxide. 2009 Nov-Dec;21(3-4):226-33. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2009.09.005. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Nitric Oxide. 2009. PMID: 19800018 Free PMC article.
-
CAPON modulates neuronal calcium handling and cardiac sympathetic neurotransmission during dysautonomia in hypertension.Hypertension. 2015 Jun;65(6):1288-1297. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05290. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25916729 Free PMC article.
-
The Physiological Function of nNOS-Associated CAPON Proteins and the Roles of CAPON in Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15808. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115808. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A common genetic variant in the NOS1 regulator NOS1AP modulates cardiac repolarization.Nat Genet. 2006 Jun;38(6):644-51. doi: 10.1038/ng1790. Epub 2006 Apr 30. Nat Genet. 2006. PMID: 16648850
-
Nitric Oxide Synthase 1 Adaptor Protein, an Emerging New Genetic Marker for QT Prolongation and Sudden Cardiac Death.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2013 May;29(3):217-25. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2013. PMID: 27122710 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Ion Channel Function by Gas Molecules.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1349:139-164. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-4254-8_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 35138614 Review.
-
NOS1AP variant associated with incidence of type 2 diabetes in calcium channel blocker users in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study.Diabetologia. 2010 Mar;53(3):510-6. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1608-0. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Diabetologia. 2010. PMID: 19943157 Free PMC article.
-
Protein S-nitrosylation in health and disease: a current perspective.Trends Mol Med. 2009 Sep;15(9):391-404. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2009.06.007. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Trends Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19726230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-induced long QT syndrome.Pharmacol Rev. 2010 Dec;62(4):760-81. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003723. Pharmacol Rev. 2010. PMID: 21079043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide association studies and contribution to cardiovascular physiology.Physiol Genomics. 2015 Sep;47(9):365-75. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00004.2015. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Physiol Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26106147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arking D-E, et al. A common genetic variant in the NOS1 regulator NOS1AP modulates cardiac repolarization. Nat Genet. 2006;38:644–651. - PubMed
-
- Aarnoudse A-J, et al. Common NOS1AP variants are associated with a prolonged QTc interval in the Rotterdam study. Circulation. 2007;116:10–16. - PubMed
-
- Jaffrey S-R, Snowman A-M, Eliasson M-J, Cohen N-A, Snyder S-H. CAPON: A protein associated with neuronal nitric oxide synthase that regulates its interactions with PSD95. Neuron. 1998;20:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Fang M, et al. Dexras1: A G protein specifically coupled to neuronal nitric oxide synthase via CAPON. Neuron. 2000;28:183–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

