Generation of antiviral major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted T cells in the absence of CD8 coreceptors
- PMID: 18337581
- PMCID: PMC2346753
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02698-07
Generation of antiviral major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted T cells in the absence of CD8 coreceptors
Abstract
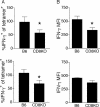
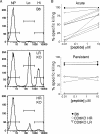
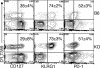
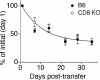
The CD8 coreceptor is important for positive selection of major histocompatibility complex I (MHC-I)-restricted thymocytes and in the generation of pathogen-specific T cells. However, the requirement for CD8 in these processes may not be essential. We previously showed that mice lacking beta(2)-microglobulin are highly susceptible to tumors induced by mouse polyoma virus (PyV), but CD8-deficient mice are resistant to these tumors. In this study, we show that CD8-deficient mice also control persistent PyV infection as efficiently as wild-type mice and generate a substantial virus-specific, MHC-I-restricted, T-cell response. Infection with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), which is acutely cleared, also recruited antigen-specific, MHC-I-restricted T cells in CD8-deficient mice. Yet, unlike in VSV infection, the antiviral MHC-I-restricted T-cell response to PyV has a prolonged expansion phase, indicating a requirement for persistent infection in driving T-cell inflation in CD8-deficient mice. Finally, we show that the PyV-specific, MHC-I-restricted T cells in CD8-deficient mice, while maintained long term at near-wild-type levels, are short lived in vivo and have extremely narrow T-cell receptor repertoires. These findings provide a possible explanation for the resistance of CD8-deficient mice to PyV-induced tumors and have implications for the maintenance of virus-specific MHC-I-restricted T cells during persistent infection.
Figures



References
-
- Allison, A. C., and L. W. Law. 1968. Effects of antilymphocyte serum on virus oncogenesis. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 127207-212. - PubMed
-
- Andrews, N. P., C. D. Pack, V. Vezys, G. N. Barber, and A. E. Lukacher. 2007. Early virus-associated bystander events affect the fitness of the CD8 T cell response to persistent virus infection. J. Immunol. 1787267-7275. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann, M. F., A. Oxenius, T. W. Mak, and R. M. Zinkernagel. 1995. T cell development in CD8−/− mice. Thymic positive selection is biased toward the helper phenotype. J. Immunol. 1553727-3733. - PubMed
-
- Berke, Z., T. Wen, G. Klein, and T. Dalianis. 1996. Polyoma tumor development in neonatally polyoma-virus-infected CD4−/− and CD8−/− single knockout and CD4−/−8−/− double knockout mice. Int. J. Cancer 67405-408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

