Transcription factor GATA-3 regulates the transcriptional activity of dopamine beta-hydroxylase by interacting with Sp1 and AP4
- PMID: 18338249
- PMCID: PMC2712938
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-008-9639-3
Transcription factor GATA-3 regulates the transcriptional activity of dopamine beta-hydroxylase by interacting with Sp1 and AP4
Abstract
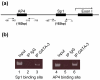
GATA-3 is a zinc finger transcription factor that is expressed in T cell lineages as well as in the nervous system during development. In this study, we report that forced expression of GATA-3 resulted in an increased number of dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH)-expressing neurons in primary neural crest stem cell (NCSC) culture, suggesting that the DBH gene may be a downstream target gene of GATA-3. GATA-3 robustly transactivates the promoter function of the noradrenaline (NA)-synthesizing DBH gene, via two specific upstream promoter domains; one at -62 to -32 bp and the other at -891 to -853 bp. Surprisingly, none of these domains contain GATA-3 binding sites but encompass binding motifs for transcription factors Sp1 and AP4, respectively. Protein-protein interaction analyses both in vitro and in vivo and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays showed that GATA-3 effects its transcriptional regulatory function through physical interactions with these transcription factors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Noradrenergic-specific transcription of the dopamine beta-hydroxylase gene requires synergy of multiple cis-acting elements including at least two Phox2a-binding sites.J Neurosci. 1998 Oct 15;18(20):8247-60. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-20-08247.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9763470 Free PMC article.
-
GATA-3 regulates the transcriptional activity of tyrosine hydroxylase by interacting with CREB.J Neurochem. 2006 Aug;98(3):773-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03924.x. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16893419
-
GATA-4 and GATA-6 modulate tissue-specific transcription of the human gene for P450c17 by direct interaction with Sp1.Mol Endocrinol. 2004 May;18(5):1144-57. doi: 10.1210/me.2003-0342. Epub 2004 Feb 26. Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 14988427
-
Regulation of the tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine beta-hydroxylase genes by the transcription factor AP-2.J Neurochem. 2001 Jan;76(1):280-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00044.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11146001
-
Transcriptional regulation by zinc-finger proteins Sp1 and MAZ involves interactions with the same cis-elements.Int J Mol Med. 2003 May;11(5):547-53. Int J Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 12684688 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression analysis of prestin and selected transcription factors in newborn rats.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Oct;31(7):1089-101. doi: 10.1007/s10571-011-9708-z. Epub 2011 May 26. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21614551 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulation of Cytokine Networks in Hippocampal CA1 Differentiates Extinction from Those Required for the Maintenance of Contextual Fear Memory after Recall.PLoS One. 2016 May 25;11(5):e0153102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153102. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27224427 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling of lymphoblasts from autistic and nonaffected sib pairs: altered pathways in neuronal development and steroid biosynthesis.PLoS One. 2009 Jun 3;4(6):e5775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005775. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19492049 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary quantitative proteomics reveals that transcription factor AP-4 mediates E-box-dependent complex formation for transcriptional repression of HDM2.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 Sep;8(9):2034-50. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900013-MCP200. Epub 2009 Jun 7. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19505873 Free PMC article.
-
TransSynW: A single-cell RNA-sequencing based web application to guide cell conversion experiments.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021 Feb;10(2):230-238. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0227. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33125830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson DJ. Lineages and transcription factors in the specification of vertebrate primary sensory neurons. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1999;9:517–524. - PubMed
-
- Edlund T, Jessell TM. Progression from extrinsic to intrinsic signaling in cell fate specification: a view from the nervous system. Cell. 1999;96:211–224. - PubMed
-
- Goridis C, Rohrer H. Specification of catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:531–541. - PubMed
-
- Marquardt T, Pfaff SL. Cracking the transcriptional code for cell specification in the neural tube. Cell. 2001;106:651–654. - PubMed
-
- Brunet JF, Pattyn A. Phox2 genes - from patterning to connectivity. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002;12:435–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

