Thyronamines are isozyme-specific substrates of deiodinases
- PMID: 18339710
- PMCID: PMC2734495
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2007-1678
Thyronamines are isozyme-specific substrates of deiodinases
Abstract
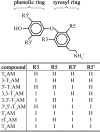
3-Iodothyronamine (3-T 1 AM) and thyronamine (T AM) are novel endogenous signaling molecules that exhibit great structural similarity to thyroid hormones but apparently antagonize classical thyroid hormone (T(3)) actions. Their proposed biosynthesis from thyroid hormones would require decarboxylation and more or less extensive deiodination. Deiodinases (Dio1, Dio2, and Dio3) catalyze the removal of iodine from their substrates. Because a role of deiodinases in thyronamine biosynthesis requires their ability to accept thyronamines as substrates, we investigated whether thyronamines are converted by deiodinases. Thyronamines were incubated with isozyme-specific deiodinase preparations. Deiodination products were analyzed using a newly established method applying liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Phenolic ring deiodinations of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronamine (rT3AM), 3',5'-diiodothyronamine (3',5'-T2AM), and 3,3'-diiodothyronamine (3,3'-T2AM) as well as tyrosyl ring deiodinations of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronamine (T3AM) and 3,5-diiodothyronamine (3,5-T2AM) were observed with Dio1. These reactions were completely inhibited by the Dio1-specific inhibitor 6n-propyl-2-thiouracil (PTU). Dio2 containing preparations also deiodinated rT(3)AM and 3',5'-T2AM at the phenolic rings but in a PTU-insensitive fashion. All thyronamines with tyrosyl ring iodine atoms were 5(3)-deiodinated by Dio3-containing preparations. In functional competition assays, the newly identified thyronamine substrates inhibited an established iodothyronine deiodination reaction. By contrast, thyronamines that had been excluded as deiodinase substrates in LC-MS/MS experiments failed to show any effect in the competition assays, thus verifying the former results. These data support a role for deiodinases in thyronamine biosynthesis and contribute to confining the biosynthetic pathways for 3-T 1 AM and T 0 AM.
Figures



References
-
- Scanlan TS, Suchland KL, Hart ME, Chiellini G, Huang Y, Kruzich PJ, Frascarelli S, Crossley DA, Bunzow JR, Ronca-Testoni S, Lin ET, Hatton D, Zucchi R, Grandy DK 2004 3-Iodothyronamine is an endogenous and rapid-acting derivative of thyroid hormone. Nat Med 10:638–642 - PubMed
-
- Chiellini G, Frascarelli S, Ghelardoni S, Carnicelli V, Tobias SC, Debarber A, Brogioni S, Ronca-Testoni S, Cerbai E, Grandy DK, Scanlan TS, Zucchi R 2007 Cardiac effects of 3-iodothyronamine: a new aminergic system modulating cardiac function. FASEB J 21:1597–1608 - PubMed
-
- Weatherman RV 2007 A triple play for thyroid hormone. ACS Chem Biol 2:377–379 - PubMed
-
- Wu SY, Green WL, Huang WS, Hays MT, Chopra IJ 2005 Alternate pathways of thyroid hormone metabolism. Thyroid 15:943–958 - PubMed
-
- Kohrle J 2002 Iodothyronine deiodinases. Methods Enzymol 347:125–167 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

