Prokineticin 1 signaling and gene regulation in early human pregnancy
- PMID: 18339712
- PMCID: PMC2696030
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2007-1633
Prokineticin 1 signaling and gene regulation in early human pregnancy
Abstract
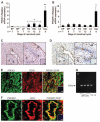
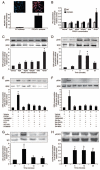
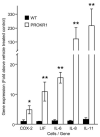
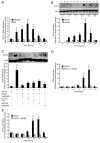
Prokineticin 1 (PROK1) is a recently described protein with a wide range of functions including tissue-specific angiogenesis, modulation of inflammatory responses, and regulation of hematopoiesis. The objective of this study was to investigate the role of PROK1 and prokineticin receptor 1 (PROKR1) in human endometrium during early pregnancy. PROK1 and PROKR1 expression is significantly elevated in first-trimester decidua, compared with nonpregnant endometrium. Expression of PROK1 and PROKR1 was localized in glandular epithelial and various cellular compartments within the stroma. To investigate the signaling pathways and target genes activated by PROK1, we generated an endometrial epithelial cell line stably expressing PROKR1 (Ishikawa PROKR1 cells). PROK1-PROKR1 interaction induced inositol phosphate mobilization and sequential phosphorylation of c-Src, epidermal growth factor receptor, and ERK 1/2. Gene microarray analysis on RNA extracted from Ishikawa PROKR1 cells treated with 40 nm PROK1 for 8 h revealed 49 genes to be differentially regulated. A number of these genes, including cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, leukemia inhibitory factor, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-11 are regulated in the endometrium during implantation and early pregnancy. We subsequently investigated the effect of PROK1 on expression of COX-2 in Ishikawa PROKR1 cells and first-trimester decidua. COX-2 mRNA and protein expression, and prostaglandin synthesis, were elevated in response to treatment with PROK1. Moreover, expression of COX-2 by PROK1 was dependent on activation of the Gq-phospholipase C-beta-cSrc-epidermal growth factor receptor-MAPK/ERK kinase pathway. These data demonstrate that PROK1 and PROKR1 expression is elevated in human decidua during early pregnancy and that PROK1-PROKR1 interaction regulates expression of a host of implantation-related genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prokineticin-1 (PROK1) modulates interleukin (IL)-11 expression via prokineticin receptor 1 (PROKR1) and the calcineurin/NFAT signalling pathway.Mol Hum Reprod. 2010 Mar;16(3):158-69. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gap084. Epub 2009 Oct 3. Mol Hum Reprod. 2010. PMID: 19801577 Free PMC article.
-
CTGF expression is up-regulated by PROK1 in early pregnancy and influences HTR-8/Svneo cell adhesion and network formation.Hum Reprod. 2011 Jan;26(1):67-75. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deq294. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Hum Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21098624 Free PMC article.
-
Prokineticin 1 induces Dickkopf 1 expression and regulates cell proliferation and decidualization in the human endometrium.Mol Hum Reprod. 2011 Oct;17(10):626-36. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gar031. Epub 2011 May 5. Mol Hum Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21546446 Free PMC article.
-
Prokineticin1 and pregnancy.Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2016 Jun;77(2):101-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2016.04.014. Epub 2016 May 9. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2016. PMID: 27172869 Review.
-
Prokineticins in angiogenesis and cancer.Cancer Lett. 2010 Oct 28;296(2):144-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.06.011. Epub 2010 Jul 14. Cancer Lett. 2010. PMID: 20633984 Review.
Cited by
-
Current knowledge of the aetiology of human tubal ectopic pregnancy.Hum Reprod Update. 2010 Jul-Aug;16(4):432-44. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmp057. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Hum Reprod Update. 2010. PMID: 20071358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Common Variant of PROK1 (V67I) Acts as a Genetic Modifier in Early Human Pregnancy through Down-Regulation of Gene Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 27;17(2):162. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020162. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26828479 Free PMC article.
-
Prokineticin-1 (PROK1) modulates interleukin (IL)-11 expression via prokineticin receptor 1 (PROKR1) and the calcineurin/NFAT signalling pathway.Mol Hum Reprod. 2010 Mar;16(3):158-69. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gap084. Epub 2009 Oct 3. Mol Hum Reprod. 2010. PMID: 19801577 Free PMC article.
-
Prokineticin 1 induces a pro-inflammatory response in murine fetal membranes but does not induce preterm delivery.Reproduction. 2013 Oct 23;146(6):581-91. doi: 10.1530/REP-13-0295. Print 2013 Dec. Reproduction. 2013. PMID: 24051059 Free PMC article.
-
Smoke, alcohol and drug addiction and female fertility.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2020 Mar 12;18(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12958-020-0567-7. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32164734 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li M, Bullock CM, Knauer DJ, Ehlert FJ, Zhou QY. Identification of two prokineticin cDNAs: recombinant proteins potently contract gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 2001;59:692–698. - PubMed
-
- LeCouter J, Kowalski J, Foster J, Hass P, Zhang Z, Dillard-Telm L, Frantz G, Rangell L, DeGuzman L, Keller GA, Peale F, Gurney A, Hillan KJ, Ferrara N. Identification of an angiogenic mitogen selective for endocrine gland endothelium. Nature. 2001;412:877–884. - PubMed
-
- Mollay C, Wechselberger C, Mignogna G, Negri L, Melchiorri P, Barra D, Kreil G. Bv8, a small protein from frog skin and its homologue from snake venom induce hyperalgesia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;374:189–196. - PubMed
-
- Lin DC, Bullock CM, Ehlert FJ, Chen JL, Tian H, Zhou QY. Identification and molecular characterization of two closely related G protein-coupled receptors activated by prokineticins/endocrine gland vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:19276–19280. - PubMed
-
- Soga T, Matsumoto S, Oda T, Saito T, Hiyama H, Takasaki J, Kamohara M, Ohishi T, Matsushime H, Furuichi K. Molecular cloning and characterization of prokineticin receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;11579:173–179. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

