Effects on membrane capacitance of steroids with antagonist properties at GABAA receptors
- PMID: 18339741
- PMCID: PMC2426621
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.124768
Effects on membrane capacitance of steroids with antagonist properties at GABAA receptors
Abstract
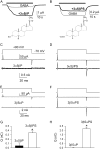
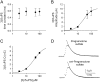
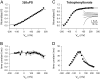
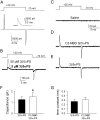
We investigated the electrophysiological signature of neuroactive steroid interactions with the plasma membrane. We found that charged, sulfated neuroactive steroids, those that exhibit noncompetitive antagonism of GABA(A) receptors, altered capacitive charge movement in response to voltage pulses in cells lacking GABA receptors. Uncharged steroids, some of which are potent enhancers of GABA(A) receptor activity, produced no alteration in membrane capacitance. We hypothesized that the charge movements might result from physical translocation of the charged steroid through the transmembrane voltage, as has been observed previously with several hydrophobic anions. However, the charge movements and relaxation time constants of capacitive currents did not exhibit the Boltzmann-type voltage dependence predicted by a single barrier model. Further, a fluorescently tagged analog of a sulfated neurosteroid altered membrane capacitance similar to the parent compound but produced no voltage-dependent fluorescence change, a result inconsistent with a strong change in the polar environment of the fluorophore during depolarization. These findings suggest that negatively charged sulfated steroids alter the plasma membrane capacitance without physical movement of the molecule through the electric field.
Figures


References
-
- Hosie, A. M., M. E. Wilkins, H. M. A. da Silva, and T. G. Smart. 2006. Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors via two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature. 444:486–489. - PubMed
-
- Majewska, M. D., J. M. Mienville, and S. Vicini. 1988. Neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate antagonizes electrophysiological responses to GABA in neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 90:279–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MH78823/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM 47969/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM047969/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012951/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA12952/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MH77791/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH078823/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012952/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- NS54174/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS44041/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS054174/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AA12951/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077791/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS044041/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

