Docosahexaenoic acid enhances segregation of lipids between : 2H-NMR study
- PMID: 18339742
- PMCID: PMC2426647
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.123612
Docosahexaenoic acid enhances segregation of lipids between : 2H-NMR study
Abstract
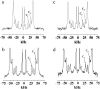
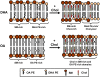
Solid-state (2)H-NMR of [(2)H(31)]-N-palmitoylsphingomyelin ([(2)H(31)]16:0SM, PSM*), supplemented by differential scanning calorimetry, was used for the first time, to our knowledge, to investigate the molecular organization of the sphingolipid in 1:1:1 mol mixtures with 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (16:0-18:1PE, POPE) or 1-palmitoyl-2-docosahexaenoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (16:0-22:6PE, PDPE) and cholesterol. When compared with (2)H-NMR data for analogous mixtures of [(2)H(31)]16:0-18:1PE (POPE*) or [(2)H(31)]16:0-22:6PE (PDPE*) with egg SM and cholesterol, molecular interactions of oleic acid (OA) versus docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are distinguished, and details of membrane architecture emerge. SM-rich, characterized by higher-order, and PE-rich, characterized by lower-order, domains <20 nm in size are formed in the absence and presence of cholesterol in both OA- and DHA-containing membranes. Although acyl chain order within both domains increases on the addition of sterol to the two systems, the resultant differential in order between SM- and PE-rich domains is almost a factor of 3 greater with DHA than with OA. Our interpretation is that the aversion that cholesterol has for DHA--but not for OA--excludes the sterol from DHA-containing, PE-rich (nonraft) domains and excludes DHA from SM-rich/cholesterol-rich (raft) domains. We attribute, in part, the diverse health benefits associated with dietary consumption of DHA to an alteration in membrane domains.
Figures




References
-
- Salem, N., Jr., B. Litman, H. Y. Kim, and K. Gawrisch. 2001. Mechanisms of action of docosahexaenoic acid in the nervous system. Lipids. 36:945–959. - PubMed
-
- Salem, N., H. Y. Kim, and J. A. Yergey. 1986. Docosahexaenoic Acid: Membrane Function and Metabolism. Academic Press, New York.
-
- Stillwell, W., and S. R. Wassall. 2003. Docosahexaenoic acid: membrane properties of a unique fatty acid. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 126:1–27. - PubMed
-
- Wassall, S. R., M. R. Brzustowicz, S. R. Shaikh, V. Cherezov, M. Caffrey, and W. Stillwell. 2004. Order from disorder, corralling cholesterol with chaotic lipids. The role of polyunsaturated lipids in membrane raft formation. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 132:79–88. - PubMed
-
- Stillwell, W., S. R. Shaikh, M. Zerouga, R. Siddiqui, and S. R. Wassall. 2005. Docosahexaenoic acid affects cell signaling by altering lipid rafts. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 45:559–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

