Cholesterol synthesis inhibition elicits an integrated molecular response in human livers including decreased ACAT2
- PMID: 18340009
- PMCID: PMC2757773
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.157172
Cholesterol synthesis inhibition elicits an integrated molecular response in human livers including decreased ACAT2
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to identify how different degrees of cholesterol synthesis inhibition affect human hepatic cholesterol metabolism.
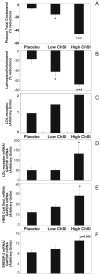
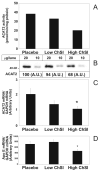
Methods and results: Thirty-seven normocholesterolemic gallstone patients randomized to treatment with placebo, 20 mg/d fluvastatin, or 80 mg/d atorvastatin for 4 weeks were studied. Based on serum lathosterol determinations, cholesterol synthesis was reduced by 42% and 70% in the 2 groups receiving statins. VLDL cholesterol was reduced by 20% and 55%. During gallstone surgery, a liver biopsy was obtained and hepatic protein and mRNA expression of rate-limiting steps in cholesterol metabolism were assayed and related to serum lipoproteins. A marked induction of LDL receptors and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG) coenzyme A (CoA) reductase was positively related to the degree of cholesterol synthesis inhibition (ChSI). The activity, protein, and mRNA for ACAT2 were all reduced during ChSI, as was apoE mRNA. The lowering of HDL cholesterol in response to high ChSI could not be explained by altered expression of the HDL receptor CLA-1, ABCA1, or apoA-I.
Conclusions: Statin treatment reduces ACAT2 activity in human liver and this effect, in combination with a reduced Apo E expression, may contribute to the favorable lowering of VLDL cholesterol seen in addition to the LDL lowering during statin treatment.
Figures
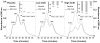

References
-
- Gotto AM., Jr Management of dyslipidemia. Am J Med. 2002;112 8A:10S–18S. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 1997;89:331–340. - PubMed
-
- Pedersen TR, Faergeman O, Kastelein JJ, Olsson AG, Tikkanen MJ, Holme I, Larsen ML, Bendiksen FS, Lindahl C, Szarek M, Tsai J. High-dose atorvastatin vs usual-dose simvastatin for secondary prevention after myocardial infarction: the IDEAL study: a randomized controlled trial. Jama. 2005;294:2437–2445. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence JM, Reid J, Taylor GJ, Stirling C, Reckless JP. The effect of high dose atorvastatin therapy on lipids and lipoprotein subfractions in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. 2004;174:141–149. - PubMed
-
- van der Harst P, Voors AA, van Veldhuisen DJ. Intensive versus moderate lipid lowering with statins after acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:714–717. author reply 714-717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

