ALLPATHS: de novo assembly of whole-genome shotgun microreads
- PMID: 18340039
- PMCID: PMC2336810
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.7337908
ALLPATHS: de novo assembly of whole-genome shotgun microreads
Abstract
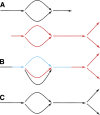
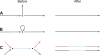
New DNA sequencing technologies deliver data at dramatically lower costs but demand new analytical methods to take full advantage of the very short reads that they produce. We provide an initial, theoretical solution to the challenge of de novo assembly from whole-genome shotgun "microreads." For 11 genomes of sizes up to 39 Mb, we generated high-quality assemblies from 80x coverage by paired 30-base simulated reads modeled after real Illumina-Solexa reads. The bacterial genomes of Campylobacter jejuni and Escherichia coli assemble optimally, yielding single perfect contigs, and larger genomes yield assemblies that are highly connected and accurate. Assemblies are presented in a graph form that retains intrinsic ambiguities such as those arising from polymorphism, thereby providing information that has been absent from previous genome assemblies. For both C. jejuni and E. coli, this assembly graph is a single edge encompassing the entire genome. Larger genomes produce more complicated graphs, but the vast majority of the bases in their assemblies are present in long edges that are nearly always perfect. We describe a general method for genome assembly that can be applied to all types of DNA sequence data, not only short read data, but also conventional sequence reads.
Figures
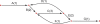
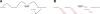


References
-
- Batzoglou S., Jaffe D.B., Stanley K., Butler J., Gnerre S., Mauceli E., Berger B., Mesirov J.P., Lander E.S., Jaffe D.B., Stanley K., Butler J., Gnerre S., Mauceli E., Berger B., Mesirov J.P., Lander E.S., Stanley K., Butler J., Gnerre S., Mauceli E., Berger B., Mesirov J.P., Lander E.S., Butler J., Gnerre S., Mauceli E., Berger B., Mesirov J.P., Lander E.S., Gnerre S., Mauceli E., Berger B., Mesirov J.P., Lander E.S., Mauceli E., Berger B., Mesirov J.P., Lander E.S., Berger B., Mesirov J.P., Lander E.S., Mesirov J.P., Lander E.S., Lander E.S. ARACHNE: A whole-genome shotgun assembler. Genome Res. 2002;12:177–189. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jeck W.R., Reinhardt J.A., Baltrus D.A., Hickenbotham M.T., Magrini V., Mardis E.R., Dangl J.L., Jones C.D., Reinhardt J.A., Baltrus D.A., Hickenbotham M.T., Magrini V., Mardis E.R., Dangl J.L., Jones C.D., Baltrus D.A., Hickenbotham M.T., Magrini V., Mardis E.R., Dangl J.L., Jones C.D., Hickenbotham M.T., Magrini V., Mardis E.R., Dangl J.L., Jones C.D., Magrini V., Mardis E.R., Dangl J.L., Jones C.D., Mardis E.R., Dangl J.L., Jones C.D., Dangl J.L., Jones C.D., Jones C.D. Extending assembly of short DNA sequences to handle error. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2942–2944. - PubMed
-
- Johnson D.S., Mortazavi A., Myers R.M., Wold B., Mortazavi A., Myers R.M., Wold B., Myers R.M., Wold B., Wold B. Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein–DNA interactions. Science. 2007;316:1497–1502. - PubMed
-
- Low G. 2004. Graphviz. http://www.graphviz.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
