Genome-wide analysis of Fis binding in Escherichia coli indicates a causative role for A-/AT-tracts
- PMID: 18340041
- PMCID: PMC2413157
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.070276.107
Genome-wide analysis of Fis binding in Escherichia coli indicates a causative role for A-/AT-tracts
Abstract
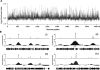
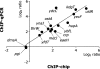
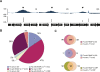
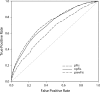
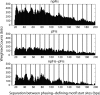
We determined the genome-wide distribution of the nucleoid-associated protein Fis in Escherichia coli using chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with high-resolution whole genome-tiling microarrays. We identified 894 Fis-associated regions across the E. coli genome. A significant number of these binding sites were found within open reading frames (33%) and between divergently transcribed transcripts (5%). Analysis indicates that A-tracts and AT-tracts are an important signal for preferred Fis-binding sites, and that A(6)-tracts in particular constitute a high-affinity signal that dictates Fis phasing in stretches of DNA containing multiple and variably spaced A-tracts and AT-tracts. Furthermore, we find evidence for an average of two Fis-binding regions per supercoiling domain in the chromosome of exponentially growing cells. Transcriptome analysis shows that approximately 21% of genes are affected by the deletion of fis; however, the changes in magnitude are small. To address the differential Fis bindings under growth environment perturbation, ChIP-chip analysis was performed using cells grown under aerobic and anaerobic growth conditions. Interestingly, the Fis-binding regions are almost identical in aerobic and anaerobic growth conditions-indicating that the E. coli genome topology mediated by Fis is superficially identical in the two conditions. These novel results provide new insight into how Fis modulates DNA topology at a genome scale and thus advance our understanding of the architectural bases of the E. coli nucleoid.
Figures
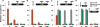

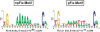
References
-
- Azam T.A., Iwata A., Nishimura A., Ueda S., Ishihama A., Iwata A., Nishimura A., Ueda S., Ishihama A., Nishimura A., Ueda S., Ishihama A., Ueda S., Ishihama A., Ishihama A. Growth phase-dependent variation in protein composition of the Escherichia coli nucleoid. J. Bacteriol. 1999;181:6361–6370. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azam T.A., Hiraga S., Ishihama A., Hiraga S., Ishihama A., Ishihama A. Two types of localization of the DNA-binding proteins within the Escherichia coli nucleoid. Genes Cells. 2000;5:613–626. - PubMed
-
- Bailey T.L., Elkan C., Elkan C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1994;2:28–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
