Toxins from cone snails: properties, applications and biotechnological production
- PMID: 18340446
- PMCID: PMC2755758
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-008-1385-6
Toxins from cone snails: properties, applications and biotechnological production
Abstract
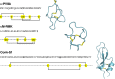
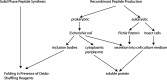
Cone snails are marine predators that use venoms to immobilize their prey. The venoms of these mollusks contain a cocktail of peptides that mainly target different voltage- and ligand-gated ion channels. Typically, conopeptides consist of ten to 30 amino acids but conopeptides with more than 60 amino acids have also been described. Due to their extraordinary pharmacological properties, conopeptides gained increasing interest in recent years. There are several conopeptides used in clinical trials and one peptide has received approval for the treatment of pain. Accordingly, there is an increasing need for the production of these peptides. So far, most individual conopeptides are synthesized using solid phase peptide synthesis. Here, we describe that at least some of these peptides can be obtained using prokaryotic or eukaryotic expression systems. This opens the possibility for biotechnological production of also larger amounts of long chain conopeptides for the use of these peptides in research and medical applications.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Sabi A, Lennartz D, Ferber M, Gulyas J, Rivier JE, Olivera BM, Carlomagno T, Terlau H. KappaM-conotoxin RIIIK, structural and functional novelty in a K channel antagonist. Biochemistry. 2004;43:8625–8635. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay PK, Colledge CJ, Walker CS, Zhou LM, Hillyard DR, Olivera BM. Conantokin-G precursor and its role in gamma-carboxylation by a vitamin K-dependent carboxylase from a Conus snail (vol 273, pg 5447, 1998) J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14658–14658. - PubMed
-
- Baneyx F. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 1999;10:411–421. - PubMed
-
- Bayrhuber M, Vijayan V, Ferber M, Graf R, Korukottu J, Imperial J, Garrett JE, Olivera BM, Terlau H, Zweckstetter M, et al. Conkunitzin-S1 is the first member of a new Kunitz-type neurotoxin family. Structural and functional characterization. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:23766–23770. - PubMed
-
- Bayrhuber M, Graf R, Ferber M, Zweckstetter M, Imperial J, Garrett JE, Olivera BM, Terlau H, Becker S. Production of recombinant Conkunitzin-S1 in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 2006;47:640–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

