Mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in rat brain induced by carbofuran exposure
- PMID: 18340526
- PMCID: PMC11515469
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-008-9270-5
Mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in rat brain induced by carbofuran exposure
Abstract
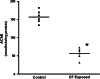
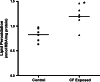
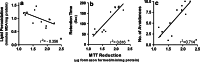
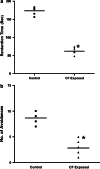
Repeated low-dose exposure to carbofuran exerts its neurotoxic effects by non-cholinergic mechanisms. Emerging evidence indicates that oxidative stress plays an important role in carbofuran neurotoxicity after sub-chronic exposure. The purpose of the present study is to evaluate the role of mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction as a primary event responsible for neurotoxic effects observed after sub-chronic carbofuran exposure. Carbofuran was administered to rats at a dose of 1 mg/kg orally for a period of 28 days. There was a significant inhibition in the activity of acetylcholinesterase (66.6%) in brain samples after 28 days of carbofuran exposure. Mitochondrial respiratory chain functions were assessed in terms of MTT (3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazolyl-2)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) reduction and activity of succinate dehydrogenase in isolated mitochondria. It was observed that carbofuran exposure significantly inhibited MTT reduction (31%) and succinate dehydrogenase activity (57%). This was accompanied by decrease in low-molecular weight thiols (66.6%) and total thiols (37.4%) and an increase in lipid peroxidation (43.7%) in the mitochondria isolated from carbofuran-exposed rat brain. The changes in mitochondrial oxidative stress and functions were associated with impaired cognitive and motor functions in the animals exposed to carbofuran as compared to the control animals. Based on these results, it is clear that carbofuran exerts its neurotoxicity by impairing mitochondrial functions leading to oxidative stress and neurobehavioral deficits.
Figures
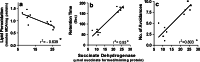
Similar articles
-
Carbofuran-induced neurochemical and neurobehavioral alterations in rats: attenuation by N-acetylcysteine.Exp Brain Res. 2006 Apr;170(4):567-75. doi: 10.1007/s00221-005-0241-5. Epub 2005 Nov 24. Exp Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16307259
-
Comparative effects of acute and chronic carbofuran exposure on oxidative stress and drug-metabolizing enzymes in liver.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2006;29(4):415-21. doi: 10.1080/01480540600837969. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16931442
-
Naringin protects memory impairment and mitochondrial oxidative damage against aluminum-induced neurotoxicity in rats.Int J Neurosci. 2013 Sep;123(9):636-45. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2013.785542. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Int J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23510099 Clinical Trial.
-
Attenuation of cellular antioxidant defense mechanisms in kidney of rats intoxicated with carbofuran.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2012 Oct;26(10):393-8. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21433. Epub 2012 Jul 16. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22807346
-
Role of aqueous extract of Cynodon dactylon in prevention of carbofuran- induced oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase inhibition in rat brain.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2011 Feb 12;57(1):135-42. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2011. PMID: 21366973
Cited by
-
Imidacloprid impedes mitochondrial function and induces oxidative stress in cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera larvae (Hubner: Noctuidae).J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2018 Feb;50(1):21-32. doi: 10.1007/s10863-017-9739-3. Epub 2018 Jan 5. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 29302769
-
Tryptophan fluorescence quenching as a binding assay to monitor protein conformation changes in the membrane of intact mitochondria.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2016 Jun;48(3):241-7. doi: 10.1007/s10863-016-9653-0. Epub 2016 Feb 23. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2016. PMID: 26905428
-
Neuroprotective potential of escitalopram against behavioral, mitochondrial and oxidative dysfunction induced by 3-nitropropionic acid.Ann Neurosci. 2015 Jan;22(1):11-8. doi: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.220104. Ann Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26124545 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of Strychnine-Induced Epilepsy Employing Amaranthus viridis L. Leaves Extract in Experimental Rats.Behav Neurol. 2023 Mar 14;2023:6684781. doi: 10.1155/2023/6684781. eCollection 2023. Behav Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36959866 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of transcriptomic responses to sub-lethal levels of six environmentally relevant pesticides in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Ecotoxicology. 2018 Sep;27(7):871-889. doi: 10.1007/s10646-018-1929-1. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Ecotoxicology. 2018. PMID: 29611082
References
-
- Barlow BK, Lee DW, Cory-Slechta DA, Opanashuk LA (2005) Modulation of antioxidant defense systems by the environmental pesticide maneb in dopaminergic cells. NeuroToxicology 26:63–75 - PubMed
-
- Bustamante J, Di Libero E, Fernandez-Cobo M, Monti N, Cadenas E, Boveris A (2004) Kinetic analysis of thapsigargin-induced thymocyte apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 37:1490–1498 - PubMed
-
- Cartmell SM, Gelgor L, Mitchell D (1991) A revised rotarod procedure for measuring the effect of antinociceptive drugs on motor function in the rat. J Pharmacol Methods 26:149–159 - PubMed
-
- Davis W Jr, Ronai Z, Tew KD (2001) Cellular thiols and reactive oxygen species in drug-induced apoptosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:1–6 - PubMed
-
- Domico LM, Zeevalk GD, Bernard LP, Cooper KR (2006) Acute neurotoxic effects of mancozeb and maneb in mesencephalic neuronal cultures are associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. NeuroToxicology 27:816–825 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

