Influence of PDZK1 on lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 18342019
- PMCID: PMC2421013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.02.004
Influence of PDZK1 on lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis
Abstract
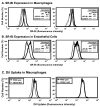
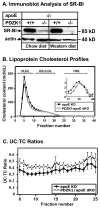
PDZK1 is a scaffold protein containing four PDZ protein interaction domains, which bind to the carboxy termini of a number of membrane transporter proteins, including ion channels (e.g., CFTR) and cell surface receptors. One of these, the HDL receptor, scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI), exhibits a striking, tissue-specific dependence on PDZK1 for its expression and activity. In PDZK1 knockout (KO) mice there is a marked reduction of SR-BI protein expression (approximately 95%) in the liver, but not in steroidogenic tissues or, as we show in this report, in bone marrow- or spleen-derived macrophages, or lung-derived endothelial cells. Because of hepatic SR-BI deficiency, PDZK1 KO mice exhibit dyslipidemia characterized by elevated plasma cholesterol carried in abnormally large HDL particles. Here, we show that inactivation of the PDZK1 gene promotes the development of aortic root atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E (apoE) KO mice fed with a high fat/high cholesterol diet. However, unlike complete SR-BI-deficiency in SR-BI/apoE double KO mice, PDZK1 deficiency in PDZK1/apoE double knockout mice did not result in development of occlusive coronary artery disease or myocardial infarction, presumably because of their residual expression of SR-BI. These findings demonstrate that deficiency of an adaptor protein essential for normal expression of a lipoprotein receptor promotes atherosclerosis in a murine model. They also define PDZK1 as a member of the family of proteins that is instrumental in preventing cardiovascular disease by maintaining normal lipoprotein metabolism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of PDZK1 causes coronary artery occlusion and myocardial infarction in Paigen diet-fed apolipoprotein E deficient mice.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 1;4(12):e8103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008103. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19956623 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted disruption of the PDZK1 gene in mice causes tissue-specific depletion of the high density lipoprotein receptor scavenger receptor class B type I and altered lipoprotein metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 26;278(52):52820-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310482200. Epub 2003 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 14551195
-
PDZK1 is required for maintaining hepatic scavenger receptor, class B, type I (SR-BI) steady state levels but not its surface localization or function.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 29;281(39):28975-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603802200. Epub 2006 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16867981
-
Role of the adaptor protein PDZK1 in controlling the HDL receptor SR-BI.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009 Jun;20(3):236-41. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32832aee82. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009. PMID: 19421056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of SR-BI-mediated high-density lipoprotein metabolism by the tissue-specific adaptor protein PDZK1.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005 Apr;16(2):147-52. doi: 10.1097/01.mol.0000162319.54795.e5. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005. PMID: 15767854 Review.
Cited by
-
Extrahepatic high-density lipoprotein receptor SR-BI and apoA-I protect against deep vein thrombosis in mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Aug;32(8):1841-7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.252130. Epub 2012 May 31. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22652597 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the PDZ3 domain of the adaptor protein PDZK1 as a second, physiologically functional binding site for the C terminus of the high density lipoprotein receptor scavenger receptor class B type I.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 15;286(28):25171-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.242362. Epub 2011 May 23. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21602281 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of G protein-coupled receptor function by Na+/H+ exchange regulatory factors.Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Dec;63(4):882-900. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.004176. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21873413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic basis of atherosclerosis: insights from mice and humans.Circ Res. 2012 Jan 20;110(2):337-55. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.230854. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22267839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HBV Infection-Related PDZK1 Plays an Oncogenic Role by Regulating the PI3K-Akt Pathway and Fatty Acid Metabolism and Enhances Immunosuppression.J Immunol Res. 2022 Aug 23;2022:8785567. doi: 10.1155/2022/8785567. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36052278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcia CK, Wilund K, Arca M, Zuliani G, Fellin R, Maioli M, Calandra S, Bertolini S, Cossu F, Grishin N, Barnes R, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH. Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia caused by mutations in a putative LDL receptor adaptor protein. Science. 2001;292:1394–1398. - PubMed
-
- He G, Gupta S, Yi M, Michaely P, Hobbs HH, Cohen JC. ARH is a modular adaptor protein that interacts with the LDL receptor, clathrin and AP-2. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44044–44049. - PubMed
-
- Kumar V, Abbas A, Fuasto N. Robbin’s and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. Elsevier and Saunders; 2005.
-
- Soutar A, Naoumova R. Mechanism of disease: genetic causes of familial hypercholesterolemia. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007;4:214–215. - PubMed
-
- Zuliani G, Arca M, Signore A, Bader G, Fazio S, Chianelli M, Bellosta S, Campagna F, Montali A, Maioli M, Pacifico A, Ricci G, Fellin R. Characterization of a new form of inherited hypercholesterolemia: familial recessive hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999;19:802–809. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL052212/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI56267/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI069208/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL66105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI50631/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL-52212/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL066105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL64737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI056267/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069208/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050631/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

