Proteomic investigation on chronic bladder irritation in the rat
- PMID: 18342204
- PMCID: PMC3750729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.10.069
Proteomic investigation on chronic bladder irritation in the rat
Abstract
Objectives: Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a painful bladder syndrome associated with urinary frequency and urgency. Elusive cause of IC makes its diagnosis only possible by exclusion in many cases. In this study, we used proteomics for identifying disease-associated proteins in a rat model of chronic bladder irritation.
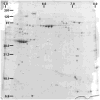
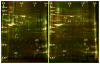
Methods: Chronic irritation of the rat bladder was caused by a brief (90 seconds) intravesical instillation of 0.2 mL of 0.4 N HCl. Whole bladders were collected at different time points after treatment, snap frozen, and nuclear and cytosolic protein extracts were obtained. Samples were resolved in standard 2-dimensional (2D) gels stained with an improved Coomasie stain or by differential gel electrophoresis (DIGE). Differentially expressed spots were excised and identified by MALDI-TOF MS/MS. Histologic and Western blot analyses were also performed.
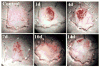
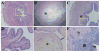
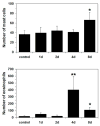
Results: Bladder morphology and histologic appearance of bladder sections after HCl treatment reflected hemorrhage, edema, epithelial denudation, detrusor mastocytosis, and eosinophilia. Proteomic analysis of irritated rat bladder revealed marked overexpression of 4 nuclear proteins and marked underexpression of 1 nuclear protein compared with normal rat bladders. Among these proteins, inflammation-associated calgranulin A (over) and smooth muscle protein-22/transgelin (under) showed opposed expression patterns after bladder irritation.
Conclusions: Presence of mast cells and eosinophils and overexpression of calgranulin A confirm the inflammatory component of HCl-irritated bladder. Altered expression of nuclear proteins is of particular interest because of their possible role as a prognostic marker in inflammatory bladder disorders. However, more studies are needed before clinical application of these findings can be established.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spinal cord injury markedly altered protein expression patterns in the affected rat urinary bladder during healing stages.J Korean Med Sci. 2011 Jun;26(6):814-23. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.6.814. Epub 2011 May 18. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21655070 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular marker for development of interstitial cystitis in rat model: isoactin gene expression.J Urol. 1997 May;157(5):1937-40. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(01)64905-x. J Urol. 1997. PMID: 9112567
-
Effects of long-term ketamine administration on rat bladder protein levels: a proteomic investigation using two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis system.Int J Urol. 2013 Oct;20(10):1024-31. doi: 10.1111/iju.12100. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Int J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23379290
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of sea buckthorn in an HCl-induced cystitis rat model.Investig Clin Urol. 2025 Jan;66(1):67-73. doi: 10.4111/icu.20240196. Investig Clin Urol. 2025. PMID: 39791586 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell involvement in interstitial cystitis: a review of human and experimental evidence.Urology. 2001 Jun;57(6 Suppl 1):47-55. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(01)01129-3. Urology. 2001. PMID: 11378050 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Urinary Cytokine and Chemokine Levels for Identifying Bladder Conditions and Predicting Treatment Outcomes in Patients with Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2022 May 17;10(5):1149. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051149. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625885 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord injury markedly altered protein expression patterns in the affected rat urinary bladder during healing stages.J Korean Med Sci. 2011 Jun;26(6):814-23. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.6.814. Epub 2011 May 18. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21655070 Free PMC article.
-
Low energy shock wave therapy attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction and improves bladder function in HCl induced cystitis in rats.Biomed J. 2022 Jun;45(3):482-490. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.06.006. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Biomed J. 2022. PMID: 34224911 Free PMC article.
-
Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Novel Treatments of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 23;10(10):2380. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102380. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complicated urinary tract infection is associated with uroepithelial expression of proinflammatory protein S100A8.Infect Immun. 2009 Oct;77(10):4265-74. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00458-09. Epub 2009 Aug 10. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19667050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drabik A, Bierczynska-Krzysik A, Bodzon-Kulakowska A, Suder P, Kotlinska J, Silberring J. Proteomics in neurosciences. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Parsons CL, Greene RA, Chung M, Stanford EJ, Singh G. Abnormal urinary potassium metabolism in patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2005;173:1182–5. - PubMed
-
- Erickson DR, Tomaszewski JE, Kunselman AR, Bentley CM, Peters KM, Rovner ES, Demers LM, Wheeler MA, Keay SK. Do the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases cystoscopic criteria associate with other clinical and objective features of interstitial cystitis? J Urol. 2005;173:93–7. - PubMed
-
- Green M, Filippou A, Sant G, Theoharides TC. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecules in the bladder of patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology. 2004;63:688–93. - PubMed
-
- Slobodov G, Feloney M, Gran C, Kyker KD, Hurst RE, Culkin DJ. Abnormal expression of molecular markers for bladder impermeability and differentiation in the urothelium of patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2004;171:1554–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

