SLC9A6 mutations cause X-linked mental retardation, microcephaly, epilepsy, and ataxia, a phenotype mimicking Angelman syndrome
- PMID: 18342287
- PMCID: PMC2427207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.01.013
SLC9A6 mutations cause X-linked mental retardation, microcephaly, epilepsy, and ataxia, a phenotype mimicking Angelman syndrome
Abstract
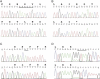
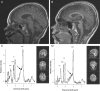
Linkage analysis and DNA sequencing in a family exhibiting an X-linked mental retardation (XLMR) syndrome, characterized by microcephaly, epilepsy, ataxia, and absent speech and resembling Angelman syndrome, identified a deletion in the SLC9A6 gene encoding the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE6. Subsequently, other mutations were found in a male with mental retardation (MR) who had been investigated for Angelman syndrome and in two XLMR families with epilepsy and ataxia, including the family designated as having Christianson syndrome. Therefore, mutations in SLC9A6 cause X-linked mental retardation. Additionally, males with findings suggestive of unexplained Angelman syndrome should be considered as potential candidates for SLC9A6 mutations.
Figures

References
-
- Chiurazzi P., Hamel B.C., Neri G. XLMR genes: Update 2000. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2001;9:71–81. - PubMed
-
- Chiurazzi, P., Schwartz, C.E., Gecz, J., and Neri, G. XLMR genes: Update 2007. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201994. - PubMed
-
- Williams C.A., Beaudet A.L., Clayton-Smith J., Knoll J.H., Kyllerman M., Laan L.A., Magenis R.E., Moncla A., Schinzel A.A., Summers J.A. Angelman syndrome 2005: Updated consensus for diagnostic criteria. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2006;140:413–418. - PubMed
-
- Williams C.A., Angelman H., Clayton-Smith J., Driscoll D.J., Hendrickson J.E., Knoll J.H., Magenis R.E., Schinzel A., Wagstaff J., Whidden E.M. Angelman syndrome: Consensus for diagnostic criteria. Angelman Syndrome Foundation. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1995;56:237–238. - PubMed
-
- Laan L.A., Vein A.A. Angelman syndrome: Is there a characteristic EEG? Brain Dev. 2005;27:80–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

