Activation of ubiquitin-dependent DNA damage bypass is mediated by replication protein a
- PMID: 18342608
- PMCID: PMC2507760
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.016
Activation of ubiquitin-dependent DNA damage bypass is mediated by replication protein a
Abstract
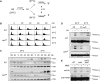
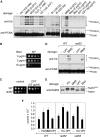
Replicative DNA damage bypass, mediated by the ubiquitylation of the sliding clamp protein PCNA, facilitates the survival of a cell in the presence of genotoxic agents, but it can also promote genomic instability by damage-induced mutagenesis. We show here that PCNA ubiquitylation in budding yeast is activated independently of the replication-dependent S phase checkpoint but by similar conditions involving the accumulation of single-stranded DNA at stalled replication intermediates. The ssDNA-binding replication protein A (RPA), an essential complex involved in most DNA transactions, is required for damage-induced PCNA ubiquitylation. We found that RPA directly interacts with the ubiquitin ligase responsible for the modification of PCNA, Rad18, both in yeast and in mammalian cells. Association of the ligase with chromatin is detected where RPA is most abundant, and purified RPA can recruit Rad18 to ssDNA in vitro. Our results therefore implicate the RPA complex in the activation of DNA damage tolerance.
Figures



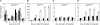

References
-
- Branzei D., Foiani M. The DNA damage response during DNA replication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005;17:568–575. - PubMed
-
- Chang D.J., Lupardus P.J., Cimprich K.A. Monoubiquitination of proliferating cell nuclear antigen induced by stalled replication requires uncoupling of DNA polymerase and mini-chromosome maintenance helicase activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:32081–32088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

