Function and structure of lipid storage droplet protein 1 studied in lipoprotein complexes
- PMID: 18342616
- PMCID: PMC2739406
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.02.036
Function and structure of lipid storage droplet protein 1 studied in lipoprotein complexes
Abstract
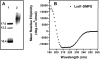
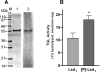
Triglycerides (TG) stored in lipid droplets (LDs) are the main energy reserve in all animals. The mechanism by which animals mobilize TG is complex and not fully understood. Several proteins surrounding the LDs have been implicated in TG homeostasis such as mammalian perilipin A and insect lipid storage proteins (Lsd). Most of the knowledge on LD-associated proteins comes from studies using cells or LDs leaving biochemical properties of these proteins uncharacterized. Here we describe the purification of recombinant Lsd1 and its reconstitution with lipids to form lipoprotein complexes suitable for functional and structural studies. Lsd1 in the lipid bound state is a predominately alpha-helical protein. Using lipoprotein complexes containing triolein it is shown that PKA mediated phosphorylation of Lsd1 promoted a 1.7-fold activation of the main fat body lipase demonstrating the direct link between Lsd1 phosphorylation and activation of lipolysis. Serine 20 was identified as the Lsd1-phosphorylation site triggering this effect.
Figures


References
-
- Wolins NE, Brasaemle DL, Bickel PE. A proposed model of fat packaging by exchangeable lipid droplet proteins. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:5484–5491. - PubMed
-
- Ziegler R, Van Antwerpen R. Lipid uptake by insect oocytes. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;36:264–272. - PubMed
-
- Beenakkers AM, Van der Horst DJ, Van Marrewijk WJ. Insect lipids and lipoproteins, and their role in physiological processes. Prog Lipid Res. 1985;24:19–67. - PubMed
-
- Brasaemle DL. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet proteins: Stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis. J Lipid Res. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Murphy DJ. The biogenesis and functions of lipid bodies in animals, plants and microorganisms. Prog Lipid Res. 2001;40:325–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

