Sox8 is a critical regulator of adult Sertoli cell function and male fertility
- PMID: 18342849
- PMCID: PMC2375044
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.01.042
Sox8 is a critical regulator of adult Sertoli cell function and male fertility
Abstract
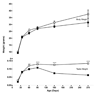
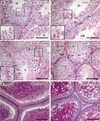
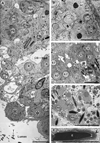
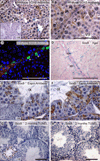
Sox8 encodes a high-mobility group transcription factor that is widely expressed during development. Sox8, -9 and -10 form group E of the Sox gene family which has been implicated in several human developmental disorders. In contrast to other SoxE genes, the role of Sox8 is unclear and Sox8 mouse mutants reportedly showed only idiopathic weight loss and reduced bone density. The careful analysis of our Sox8 null mice, however, revealed a progressive male infertility phenotype. Sox8 null males only sporadically produced litters of reduced size at young ages. We have shown that SOX8 protein is a product of adult Sertoli cells and its elimination results in an age-dependent deregulation of spermatogenesis, characterized by sloughing of spermatocytes and round spermatids, spermiation failure and a progressive disorganization of the spermatogenic cycle, which resulted in the inappropriate placement and juxtaposition of germ cell types within the epithelium. Those sperm that did enter the epididymides displayed abnormal motility. These data show that SOX8 is a critical regulator of adult Sertoli cell function and is required for both its cytoarchitectural and paracrine interactions with germ cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sox8 and Sertoli-cell function.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Dec;1120:104-13. doi: 10.1196/annals.1411.007. Epub 2007 Sep 28. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17905940
-
Genome-wide identification of Sox8-, and Sox9-dependent genes during early post-natal testis development in the mouse.Andrology. 2013 Mar;1(2):281-92. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-2927.2012.00049.x. Epub 2013 Jan 13. Andrology. 2013. PMID: 23315995
-
Downstream genes of Sox8 that would affect adult male fertility.Sex Dev. 2009;3(1):16-25. doi: 10.1159/000200078. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Sex Dev. 2009. PMID: 19339814 Free PMC article.
-
Origin and possible roles of the Sox8 transcription factor gene during sexual development.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003;101(3-4):212-8. doi: 10.1159/000074339. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003. PMID: 14689607 Review.
-
SOX E genes: SOX9 and SOX8 in mammalian testis development.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Mar;42(3):433-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.07.015. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19647095 Review.
Cited by
-
Expressions of Sox9, Sox5, and Sox13 transcription factors in mice testis during postnatal development.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Sep;407(1-2):209-21. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2470-7. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26045173
-
Mammalian sex determination—insights from humans and mice.Chromosome Res. 2012 Jan;20(1):215-38. doi: 10.1007/s10577-012-9274-3. Chromosome Res. 2012. PMID: 22290220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Case of Agonadism, Skeletal Malformations, Bicuspid Aortic Valve, and Delayed Development with a 16p13.3 Duplication Including GNG13 and SOX8 Upstream Enhancers: Are Either, Both or Neither Involved in the Phenotype?Mol Syndromol. 2011 Jan;1(4):185-191. doi: 10.1159/000321957. Epub 2010 Nov 13. Mol Syndromol. 2011. PMID: 21373258 Free PMC article.
-
The replaceable master of sex determination: bottom-up hypothesis revisited.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021 Aug 30;376(1832):20200090. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0090. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34247496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genome-wide association study in Chinese men identifies three risk loci for non-obstructive azoospermia.Nat Genet. 2011 Dec 25;44(2):183-6. doi: 10.1038/ng.1040. Nat Genet. 2011. PMID: 22197933
References
-
- Beardsley A, O'Donnell L. Characterization of normal spermiation and spermiation failure induced by hormone suppression in adult rats. Biol. Reprod. 2003;68:1299–1307. - PubMed
-
- Bondurand N, et al. A molecular analysis of the yemenite deaf-blind hypopigmentation syndrome: SOX10 dysfunction causes different neurocristopathies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999;8:1785–1789. - PubMed
-
- Bowles J, et al. Phylogeny of the SOX family of developmental transcription factors based on sequence and structural indicators. Dev. Biol. 2000;227:239–255. - PubMed
-
- Cameron D, Griffin F. Ultrastructure of Sertoli-germ cell interactions in the normal and pathologic testis. In: M-GF R, editor. Male Reproduction: A multidisciplinary overview. Spain: Churchill; 1998. pp. 229–242.
-
- Chaboissier MC, et al. Functional analysis of Sox8 and Sox9 during sex determination in the mouse. Development. 2004;131:1891–1901. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

