Aging and hormones of the hypothalamo-pituitary axis: gonadotropic axis in men and somatotropic axes in men and women
- PMID: 18343203
- PMCID: PMC2583117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2007.12.005
Aging and hormones of the hypothalamo-pituitary axis: gonadotropic axis in men and somatotropic axes in men and women
Abstract
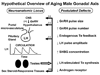
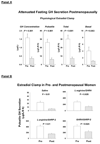
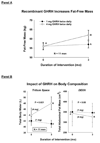
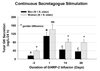
Neuroendocrinology of the aging (male) gonadal and (male and female) somatotropic axes will be reviewed. A companion chapter discusses reproductive hormonal changes in aging women. Both the gonadal and growth-hormone/insulin-like growth factor (GH/IGF-I) axes function as ensembles. The ensembles comprise tripartite interactions among the brain (hypothalamus), anterior pituitary gland (gonadotrope and somatotrope cells) and target organs (testis, liver, muscle, fat and brain). Compelling evidence indicates that combined hypothalamic and gonadal adaptations operate in the reproductive axis of older men, and multiple hypothalamic adaptations prevail in the GH axis of elderly men and women. Evolving investigative methods allow more precise parsing of the particular mechanisms that subserve such age-related changes, and suggest novel interventional strategies to evaluate the physiological impact of the dynamic alterations discerned in aging individuals.
Figures










References
-
- Arvat E, Ceda GP, Di Vito L, Ramunni J, Gianotti L, Ghigo E. Age-related variations in the neuroendocrine control, more than impaired receptor sensitivity, cause the reduction in the GH-releasing activity of GHRP's in human aging. Pituitary. 1998;1:51–58. - PubMed
-
- Bowers CY, Granda R, Mohan S, Kuipers J, Baylink D, Veldhuis JD. Sustained elevation of pulsatile growth hormone (GH) secretion and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), and IGFBP-5 concentrations during 30-day continuous subcutaneous infusion of GH-releasing peptide-2 in older men and women. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology Metabolism. 2004;89:2290–2300. - PubMed
-
- Brill KT, Weltman AL, Gentili A, Patrie JT, Fryburg DA, Hanks JB, Urban RJ, Veldhuis JD. Single and combined effects of growth hormone and testosterone administration on measures of body composition, physical performance, mood, sexual function, bone turnover, and muscle gene expression in healthy older men. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology Metabolism. 2002;87:5649–5657. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Maricic M, Nguyen P, Ahmann FR, Bruhn R, Dalkin BL. Low bone density and high percentage of body fat among men who were treated with androgen deprivation therapy for prostate carcinoma. Cancer. 2002;95:2136–2144. - PubMed
-
- Dufau ML, Veldhuis JD. Pathophysiological relationships between the biological and immunological activities of luteinizing hormone. 1987;1:153–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

