Detection of colonic dysplasia in vivo using a targeted heptapeptide and confocal microendoscopy
- PMID: 18345013
- PMCID: PMC3324975
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1692
Detection of colonic dysplasia in vivo using a targeted heptapeptide and confocal microendoscopy
Erratum in
- Nat Med. 2008 May;14(5):585. Hsiung, Pei-Lei [corrected to Hsiung, Pei-Lin]
Abstract
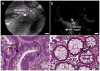
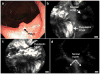
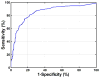
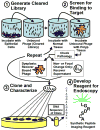
A combination of targeted probes and new imaging technologies provides a powerful set of tools with the potential to improve the early detection of cancer. To develop a probe for detecting colon cancer, we screened phage display peptide libraries against fresh human colonic adenomas for high-affinity ligands with preferential binding to premalignant tissue. We identified a specific heptapeptide sequence, VRPMPLQ, which we synthesized, conjugated with fluorescein and tested in patients undergoing colonoscopy. We imaged topically administered peptide using a fluorescence confocal microendoscope delivered through the instrument channel of a standard colonoscope. In vivo images were acquired at 12 frames per second with 50-microm working distance and 2.5-microm (transverse) and 20-microm (axial) resolution. The fluorescein-conjugated peptide bound more strongly to dysplastic colonocytes than to adjacent normal cells with 81% sensitivity and 82% specificity. This methodology represents a promising diagnostic imaging approach for the early detection of colorectal cancer and potentially of other epithelial malignancies.
Figures


References
-
- Vogelstein B, et al. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:525–32. - PubMed
-
- Winawer SJ, et al. Prevention of colorectal cancer by colonoscopic polypectomy. The National Polyp Study Workgroup. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1977–81. - PubMed
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures. 2006.
-
- Fujii T, Rembacken BJ, Dixon MF, Yoshida S, Axon AT. Flat adenomas in the United Kingdom: are treatable cancers being missed? Endoscopy. 1998;30:437–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

