Role of the carboxyl terminal di-leucine in phosphorylation and internalization of C5a receptor
- PMID: 18346468
- PMCID: PMC2430410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.02.004
Role of the carboxyl terminal di-leucine in phosphorylation and internalization of C5a receptor
Abstract
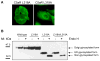
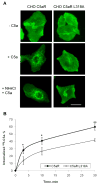
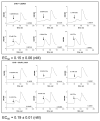
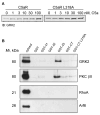
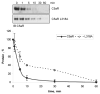
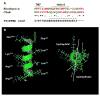
The carboxyl tail of G protein-coupled receptors contains motifs that regulate receptor interactions with intracellular partners. Activation of the human neutrophil complement fragment C5a receptor (C5aR) is terminated by phosphorylation of the carboxyl tail followed by receptor internalization. In this study, we demonstrated that bulky hydrophobic residues in the membrane-proximal region of the C5aR carboxyl tail play an important role in proper structure and function of the receptor: Substitution of leucine 319 with alanine (L319A) resulted in receptor retention in the endoplasmic reticulum, whereas a L318A substitution allowed receptor transport to the cell surface, but showed slow internalization upon activation, presumably due to a defect in phosphorylation by both PKC and GRK. Normal agonist-induced activation of ERK1/2 and intracellular calcium release suggested that the L318A mutation did not affect receptor signaling. Binding of GRK2 and PKCbetaII to intracellular loop 3 of C5aR in vitro indicated that mutagenesis of L318 did not affect kinase binding. Limited proteolysis with trypsin revealed a conformational difference between wild type and mutant receptor. Our studies support a model in which the L318/L319 stabilizes an amphipathic helix (Q305-R320) in the membrane-proximal region of C5aR.
Figures




References
-
- Reiter E, Lefkowitz RJ. GRKs and β-arrestins: roles in receptor silencing, trafficking and signaling. Trends Endocrin Metab. 2006;17:159. - PubMed
-
- Loudon RP, Perussia B, Benovic JL. Differentially regulated expression of the G-protein-coupled receptor kinases, betaARK and GRK6, during myelomonocytic cell development in vitro. Blood. 1996;88:4547. - PubMed
-
- Langkabel P, Zwirner J, Oppermann M. Ligand-induced phosphorylation of anaphylatoxin receptors C3aR and C5aR is mediated by G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29:3035. - PubMed
-
- Chuang TT, Sallese M, Ambrosini G, Parruti G, De Blasi A. High expression of β-adrenergic receptor kinase in human peripheral blood leukocytes. Isoproterenol and platelet activating factor can induce kinase translocation. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:6886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

