A house with many rooms: how the heart got its chambers with foxn4
- PMID: 18347088
- PMCID: PMC2731666
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1662408
A house with many rooms: how the heart got its chambers with foxn4
Figures
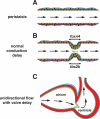
Comment on
-
Foxn4 directly regulates tbx2b expression and atrioventricular canal formation.Genes Dev. 2008 Mar 15;22(6):734-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.1629408. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18347092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basson C.T., Bachinsky D.R., Lin R.C., Levi T., Elkins J.A., Soults J., Grayzel D., Kroumpouzou E., Traill T.A., Leblanc-Straceski J., et al. Mutations in human TBX5 [corrected] cause limb and cardiac malformation in Holt-Oram syndrome. Nat. Genet. 1997;15:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Bruneau B.G., Nemer G., Schmitt J.P., Charron F., Robitaille L., Caron S., Conner D.A., Gessler M., Nemer M., Seidman C.E., et al. A murine model of Holt-Oram syndrome defines roles of the T-box transcription factor Tbx5 in cardiogenesis and disease. Cell. 2001;106:709–721. - PubMed
-
- Christoffels V.M., Hoogaars W.M., Tessari A., Clout D.E., Moorman A.F., Campione M. T-box transcription factor Tbx2 represses differentiation and formation of the cardiac chambers. Dev. Dyn. 2004;229:763–770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
