Inhibition of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA polymerase by DNA aptamers: mechanism of inhibition of in vitro RNA synthesis and effect on HCV-infected cells
- PMID: 18347106
- PMCID: PMC2415787
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01227-07
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA polymerase by DNA aptamers: mechanism of inhibition of in vitro RNA synthesis and effect on HCV-infected cells
Abstract
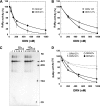
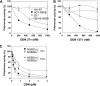
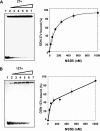
We describe here the further characterization of two DNA aptamers that specifically bind to hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA polymerase (NS5B) and inhibit its polymerase activity in vitro. Although they were obtained from the same selection procedure and contain an 11-nucleotide consensus sequence, our results indicate that aptamers 27v and 127v use different mechanisms to inhibit HCV polymerase. While aptamer 27v was able to compete with the RNA template for binding to the enzyme and blocked both the initiation and the elongation of RNA synthesis, aptamer 127v competed poorly and exclusively inhibited initiation and postinitiation events. These results illustrate the power of the selective evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment in vitro selection procedure approach to select specific short DNA aptamers able to inhibit HCV NS5B by different mechanisms. We also determined that, in addition to an in vitro inhibitory effect on RNA synthesis, aptamer 27v was able to interfere with the multiplication of HCV JFH1 in Huh7 cells. The efficient cellular entry of these short DNAs and the inhibitory effect observed on human cells infected with HCV indicate that aptamers are useful tools for the study of HCV RNA synthesis, and their use should become a very attractive and alternative approach to therapy for HCV infection.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Selection of DNA aptamers that bind the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus and inhibit viral RNA synthesis in vitro.Oligonucleotides. 2003;13(6):455-63. doi: 10.1089/154545703322860771. Oligonucleotides. 2003. PMID: 15025912
-
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication by specific RNA aptamers against HCV NS5B RNA replicase.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(12):7064-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00405-13. Epub 2013 Apr 17. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23596299 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus production by aptamers against the core protein.J Virol. 2014 Feb;88(4):1990-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03312-13. Epub 2013 Dec 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24307579 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleoside analog inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006 Mar;6(1):17-29. doi: 10.2174/187152606776056698. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16787301 Review.
-
Recent progress in the development of inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(13):1302-29. doi: 10.2174/156802607781212211. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17627559 Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamers for Anti-Viral Therapeutics and Diagnostics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 17;22(8):4168. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084168. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Subcellular Localisation of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) 16 E7 Protein in Cervical Cancer Cells and Its Perturbation by RNA Aptamers.Viruses. 2015 Jun 26;7(7):3443-61. doi: 10.3390/v7072780. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26131956 Free PMC article.
-
Bioprocess development for biosurfactant production by Natrialba sp. M6 with effective direct virucidal and anti-replicative potential against HCV and HSV.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 4;12(1):16577. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20091-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36195643 Free PMC article.
-
Oligonucleotide aptamers: potential novel molecules against viral hepatitis.Res Pharm Sci. 2017 Apr;12(2):88-98. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.202447. Res Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28515761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro and ex vivo selection procedures for identifying potentially therapeutic DNA and RNA molecules.Molecules. 2010 Jun 28;15(7):4610-38. doi: 10.3390/molecules15074610. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20657381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ago, H., T. Adachi, A. Yoshida, M. Yamamoto, N. Habuka, K. Yatsunami, and M. Miyano. 1999. Crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus. Structure 7:1417-1426. - PubMed
-
- Astier-Gin, T., P. Bellecave, S. Litvak, and M. Ventura. 2005. Template requirements and binding of hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase during in vitro RNA synthesis from the 3′-end of virus minus-strand RNA. FEBS J. 272:3872-3886. - PubMed
-
- Bellecave, P., M. L. Andreola, M. Ventura, L. Tarrago-Litvak, S. Litvak, and T. Astier-Gin. 2003. Selection of DNA aptamers that bind the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus and inhibit viral RNA synthesis in vitro. Oligonucleotides 13:455-463. - PubMed
-
- Biswal, B. K., M. M. Cherney, M. Wang, L. Chan, C. G. Yannopoulos, D. Bilimoria, O. Nicolas, J. Bedard, and M. N. G. James. 2005. Crystal structures of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase genotype 2a of hepatitis C virus reveal two conformations and suggest mechanisms of inhibition by non-nucleoside inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 280:18202-18210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

