Can essential fatty acids reduce the burden of disease(s)?
- PMID: 18348729
- PMCID: PMC2276500
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-7-9
Can essential fatty acids reduce the burden of disease(s)?
Abstract
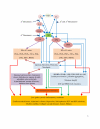
Coronary heart disease, stroke, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, cancer, depression schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, and collagen vascular diseases are low-grade systemic inflammatory conditions that are a severe burden on health care resources. Essential fatty acids (EFAs) and their metabolites: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA), and arachidonic acid (AA) and their products: prostaglandin E1, prostacyclin, lipoxins, resolvins, and protectins suppress inflammation, augment healing, and are of benefit in the prevention and management of these conditions. Hence, supplementation of EFAs could reduce burden of these disease(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Essential fatty acids and their metabolites could function as endogenous HMG-CoA reductase and ACE enzyme inhibitors, anti-arrhythmic, anti-hypertensive, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective, and cardioprotective molecules.Lipids Health Dis. 2008 Oct 15;7:37. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-7-37. Lipids Health Dis. 2008. PMID: 18922179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Cell Membrane Theory of Senescence" and the Role of Bioactive Lipids in Aging, and Aging Associated Diseases and Their Therapeutic Implications.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 8;11(2):241. doi: 10.3390/biom11020241. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33567774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential fatty acid metabolism in patients with essential hypertension, diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1995 Jun;52(6):387-91. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(95)90066-7. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1995. PMID: 7644560
-
Essential Fatty acids - a review.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2006 Dec;7(6):467-82. doi: 10.2174/138920106779116856. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 17168664 Review.
-
Essential fatty acids: biochemistry, physiology and pathology.Biotechnol J. 2006 Apr;1(4):420-39. doi: 10.1002/biot.200600012. Biotechnol J. 2006. PMID: 16892270 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential fatty acids and their metabolites could function as endogenous HMG-CoA reductase and ACE enzyme inhibitors, anti-arrhythmic, anti-hypertensive, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective, and cardioprotective molecules.Lipids Health Dis. 2008 Oct 15;7:37. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-7-37. Lipids Health Dis. 2008. PMID: 18922179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can endogenous lipid molecules serve as predictors and prognostic markers of coronary heart disease?Lipids Health Dis. 2008 May 20;7:19. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-7-19. Lipids Health Dis. 2008. PMID: 18489792 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Dietary Interventions for COVID-19 Infection Based on the Gut-Immune Axis: An Update Review on Bioactive Component of Macronutrients.Int J Prev Med. 2021 Aug 24;12:105. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_493_20. eCollection 2021. Int J Prev Med. 2021. PMID: 34729139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of somatic cell count as an indicator of colostrum quality.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 11;15(8):e0237615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237615. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32780761 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ω-3 and ω-9 fatty acid rich oils on lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenases enzymes and on the growth of a mammary adenocarcinoma model.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Oct 8;9:112. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-112. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20932327 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Das UN. Hypertension as a low-grade systemic inflammatory condition that has its origins in the perinatal period. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006;54:133–142. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

