Revisiting the Koebner phenomenon: role of NGF and its receptor system in the pathogenesis of psoriasis
- PMID: 18349121
- PMCID: PMC2276420
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070710
Revisiting the Koebner phenomenon: role of NGF and its receptor system in the pathogenesis of psoriasis
Abstract
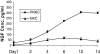
Nerve growth factor (NGF) influences the key pathological events of psoriasis: keratinocyte proliferation, angiogenesis, and T-cell activation. We have systematically examined the kinetics of NGF expression, keratinocyte proliferation, and migration of T lymphocytes in the epidermis in Koebner-induced developing psoriatic plaques. In skin traumatized by the tape-stripping method (n = 12), a marked up-regulation of NGF in Koebner-positive lesions (n = 7) was observed 24 hours after trauma. Synthesis of NGF reached its maximum level in the 2nd week. Furthermore, cultured keratinocytes from nonlesional skin of psoriasis patients produced 10 times higher levels of NGF compared with keratinocytes from healthy individuals. To substantiate the in vivo effect of NGF secreted by keratinocytes in psoriatic plaques, we studied psoriatic plaques and normal human skin in a SCID-human skin xenograft model. The transplanted psoriatic plaques demonstrated marked proliferation of NGF-R (p75)-positive nerve fibers compared with only a few nerves in the transplanted normal human skin. Our results demonstrate that 1) in a developing psoriatic lesion, up-regulation of NGF together with keratinocyte proliferation are early events and precede epidermotropism of T lymphocytes; 2) keratinocytes in patients with psoriasis are primed to produce elevated levels of NGF; and 3) NGF synthesized by these keratinocytes is functionally active.
Figures
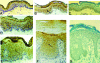
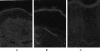

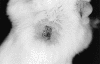

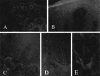
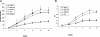
Comment in
-
Nerve growth factor: the dark side of the icon.Am J Pathol. 2008 Apr;172(4):865-7. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.080008. Epub 2008 Mar 18. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18349120 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aloe L. Nerve growth factor and neuroimmune responses: basic and clinical observations. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2001;109:354–356. - PubMed
-
- Hattori A, Iwasaki S, Murase K, Tsujiimoto M, Sato M, Hyashi K, Kohno M. Tumor necrosis factor is markedly synergistic with interleukin1 and interferon gamma in stimulating the production of nerve growth factor in fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1994;340:177–180. - PubMed
-
- Heese K, Hock C, Otten U. Inflammatory signals induce neurotrophin expression in human microglial cells. J Neurochem. 1998;70:699–707. - PubMed
-
- Farber EM, Nickoloff BJ, Recht B, Fraki JE. Stress, symmetry, and psoriasis: possible role of neuropeptides. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14:305–311. - PubMed
-
- Raychaudhuri SP, Farber EM. Are sensory nerves essential for the development of psoriasis lesions? J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:488–489. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

