Rifamycin antibiotic resistance by ADP-ribosylation: Structure and diversity of Arr
- PMID: 18349144
- PMCID: PMC2290778
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0711939105
Rifamycin antibiotic resistance by ADP-ribosylation: Structure and diversity of Arr
Abstract
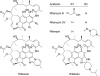
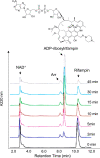
The rifamycin antibiotic rifampin is important for the treatment of tuberculosis and infections caused by multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Recent iterations of the rifampin core structure have resulted in new drugs and drug candidates for the treatment of a much broader range of infectious diseases. This expanded use of rifamycin antibiotics has the potential to select for increased resistance. One poorly characterized mechanism of resistance is through Arr enzymes that catalyze ADP-ribosylation of rifamycins. We find that genes encoding predicted Arr enzymes are widely distributed in the genomes of pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria. Biochemical analysis of three representative Arr enzymes from environmental and pathogenic bacterial sources shows that these have equally efficient drug resistance capacity in vitro and in vivo. The 3D structure of one of these orthologues from Mycobacterium smegmatis was determined and reveals structural homology with ADP-ribosyltransferases important in eukaryotic biology, including poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) and bacterial toxins, despite no significant amino acid sequence homology with these proteins. This work highlights the extent of the rifamycin resistome in microbial genera with the potential to negatively impact the expanded use of this class of antibiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

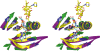
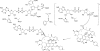
Similar articles
-
Modulation of a Mycobacterial ADP-Ribosyltransferase to Augment Rifamycin Antibiotic Resistance.ACS Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 10;7(9):2604-2611. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00297. Epub 2021 Aug 6. ACS Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34355905
-
New C25 carbamate rifamycin derivatives are resistant to inactivation by ADP-ribosyl transferases.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Jan 15;17(2):522-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.10.016. Epub 2006 Oct 12. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007. PMID: 17070048
-
Species-Specific Interactions of Arr with RplK Mediate Stringent Response in Bacteria.J Bacteriol. 2018 Feb 23;200(6):e00722-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00722-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29311276 Free PMC article.
-
The Enzymes of the Rifamycin Antibiotic Resistome.Acc Chem Res. 2021 May 4;54(9):2065-2075. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00048. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33877820 Review.
-
The ARTT motif and a unified structural understanding of substrate recognition in ADP-ribosylating bacterial toxins and eukaryotic ADP-ribosyltransferases.Int J Med Microbiol. 2002 Feb;291(6-7):523-9. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00162. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11890553 Review.
Cited by
-
Arr-cb Is a Rifampin Resistance Determinant Found Active or Cryptic in Clostridium bolteae Strains.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jul 25;61(8):e00301-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00301-17. Print 2017 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28533241 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Rifamycin-Degrading Monooxygenase From Rifamycin Producers Implicating Its Involvement in Saliniketal Biosynthesis.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jun 3;11:971. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00971. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32582048 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 May 17;10(5):593. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10050593. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of a rifampin-inactivating glycosyltransferase from a screen of environmental actinomycetes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Oct;56(10):5061-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01166-12. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22802246 Free PMC article.
-
Rifampin phosphotransferase is an unusual antibiotic resistance kinase.Nat Commun. 2016 Apr 22;7:11343. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11343. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27103605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alekshun MN, Levy SB. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell. 2007;128:1037–1050. - PubMed
-
- Wright GD. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: Enzymatic degradation and modification. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:1451–1470. - PubMed
-
- Morisaki N, et al. Structures of ADP-ribosylated rifampicin and its metabolite: Intermediates of rifampicin-ribosylation by Mycobacterium smegmatis DSM43756. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2000;53:269–275. - PubMed
-
- Imai T, et al. Identification and characterization of a new intermediate in the ribosylative inactivation pathway of rifampin by Mycobacterium smegmatis. Microb Drug Resist. 1999;5:259–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

