Anacardic acid (6-nonadecyl salicylic acid), an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase, suppresses expression of nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products involved in cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and inflammation through inhibition of the inhibitory subunit of nuclear factor-kappaBalpha kinase, leading to potentiation of apoptosis
- PMID: 18349320
- PMCID: PMC2384122
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-117994
Anacardic acid (6-nonadecyl salicylic acid), an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase, suppresses expression of nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products involved in cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and inflammation through inhibition of the inhibitory subunit of nuclear factor-kappaBalpha kinase, leading to potentiation of apoptosis
Abstract
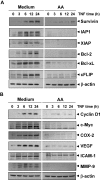
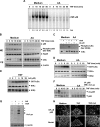
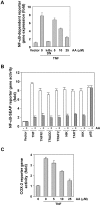
Anacardic acid (6-pentadecylsalicylic acid) is derived from traditional medicinal plants, such as cashew nuts, and has been linked to anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and radiosensitization activities through a mechanism that is not yet fully understood. Because of the role of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation in these cellular responses, we postulated that anacardic acid might interfere with this pathway. We found that this salicylic acid potentiated the apoptosis induced by cytokine and chemotherapeutic agents, which correlated with the down-regulation of various gene products that mediate proliferation (cyclin D1 and cyclooxygenase-2), survival (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, cFLIP, cIAP-1, and survivin), invasion (matrix metalloproteinase-9 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1), and angiogenesis (vascular endothelial growth factor), all known to be regulated by the NF-kappaB. We found that anacardic acid inhibited both inducible and constitutive NF-kappaB activation; suppressed the activation of IkappaBalpha kinase that led to abrogation of phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaBalpha; inhibited acetylation and nuclear translocation of p65; and suppressed NF-kappaB-dependent reporter gene expression. Down-regulation of the p300 histone acetyltransferase gene by RNA interference abrogated the effect of anacardic acid on NF-kappaB suppression, suggesting the critical role of this enzyme. Overall, our results demonstrate a novel role for anacardic acid in potentially preventing or treating cancer through modulation of NF-kappaB signaling pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Olivera Ortega AG, Soto Hernandez M, Martinez Vazquez M, Terrazas Salgado T, Solares Arenas F. Phytochemical study of cuachalalate (Amphiptherygium adstringens, Schiede ex Schlecht). J Ethnopharmacol. 1999;68:109–113. - PubMed
-
- Acevedo HR, Rojas MD, Arceo SD, et al. Effect of 6-nonadecyl salicylic acid and its methyl ester on the induction of micronuclei in polychromatic erythrocytes in mouse peripheral blood. Mutat Res. 2006;609:43–46. - PubMed
-
- Rea AI, Schmidt JM, Setzer WN, Sibanda S, Taylor C, Gwebu ET. Cytotoxic activity of Ozoroa insignis from Zimbabwe. Fitoterapia. 2003;74:732–735. - PubMed
-
- Kubo I, Kinst-Hori I, Yokokawa Y. Tyrosinase inhibitors from Anacardium occidentale fruits. J Nat Prod. 1994;57:545–551. - PubMed
-
- Itokawa H, Totsuka N, Nakahara K, Takeya K, Lepoittevin JP, Asakawa Y. Antitumor principles from Ginkgo biloba L. Chem Pharm Bull. 1987;35:3016–3020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

