Treatment of the neurogenic bladder in spina bifida
- PMID: 18350321
- PMCID: PMC2335291
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-008-0780-7
Treatment of the neurogenic bladder in spina bifida
Abstract
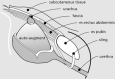
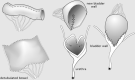
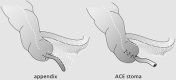
Renal damage and renal failure are among the most severe complications of spina bifida. Over the past decades, a comprehensive treatment strategy has been applied that results in minimal renal scaring. In addition, the majority of patients can be dry for urine by the time they go to primary school. To obtain such results, it is mandatory to treat detrusor overactivity from birth onward, as upper urinary tract changes predominantly start in the first months of life. This means that new patients with spina bifida should be treated from birth by clean intermittent catheterization and pharmacological suppression of detrusor overactivity. Urinary tract infections, when present, need aggressive treatment, and in many patients, permanent prophylaxis is indicated. Later in life, therapy can be tailored to urodynamic findings. Children with paralyzed pelvic floor and hence urinary incontinence are routinely offered surgery around the age of 5 years to become dry. Rectus abdominis sling suspension of the bladder neck is the first-choice procedure, with good to excellent results in both male and female patients. In children with detrusor hyperactivity, detrusorectomy can be performed as an alternative for ileocystoplasty provided there is adequate bladder capacity. Wheelchair-bound patients can manage their bladder more easily with a continent catheterizable stoma on top of the bladder. This stoma provides them extra privacy and diminishes parental burden. Bowel management is done by retrograde or antegrade enema therapy. Concerning sexuality, special attention is needed to address expectations of adolescent patients. Sensibility of the glans penis can be restored by surgery in the majority of patients.
Figures

References
-
- Pal-de Bruin KM, Buitendijk SE, Hirasing RA, den Ouden AL. Prevalence of neural tube defects in births before and after promotion of periconceptional folic acid supplementation. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2000;144(36):1732–1736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

