An open-label pilot study of the effectiveness of adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and previous infliximab treatment: relationship to reasons for failure and anti-infliximab antibody status
- PMID: 18350329
- PMCID: PMC2468311
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-008-0866-4
An open-label pilot study of the effectiveness of adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and previous infliximab treatment: relationship to reasons for failure and anti-infliximab antibody status
Abstract
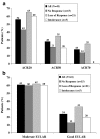
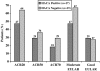
This prospective open-label pilot study evaluated the effectiveness and safety of adalimumab and the relationship to antibodies against infliximab (IFX) in adult patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had been treated previously with IFX and experienced treatment failure owing to lack or loss of response or intolerance. Patients self-administered adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneously every other week for 16 weeks, followed by maintenance therapy for up to Week 56. Measures of effectiveness included American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) response criteria, 28-joint Disease Activity Score, and the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index. Serum IFX concentrations, human antichimeric antibody against IFX (HACA), adalimumab serum concentrations, antiadalimumab antibody, and safety also were assessed. Of the 41 enrolled patients, 37 completed 16 weeks and 30 completed 56 weeks of treatment. Patients experienced clinically meaningful improvements in all measures of RA activity, with greater response rates observed for patients who had experienced loss of initial response to or intolerance of IFX. At Week 16, 46% of patients achieved an ACR20 and 28% achieved an ACR50; 61% achieved an at least moderate and 17% achieved a good EULAR response. Clinical benefit was maintained through Week 56 in all effectiveness parameters. Baseline HACA status did not significantly impact effectiveness. No new safety signals were observed; neither former IFX intolerance status nor baseline HACA status had a clinically relevant impact on adverse event frequency or severity. Adalimumab was effective and well-tolerated in patients with RA who previously failed IFX therapy, irrespective of reason for discontinuation and of HACA status.
Figures
References
-
- Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:26–37. doi: 10.1002/art.21519. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Genovese MC, Bathon JM, Fleischmann RM, et al. Long-term safety, efficacy, and radiographic outcome with etanercept treatment in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:1232–1242. - PubMed
-
- Keystone EC, Kavanaugh AF, Sharp JT, et al. Radiographic, clinical, and functional outcomes of treatment with adalimumab (a human anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving concomitant methotrexate therapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled, 52-week trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1400–1411. doi: 10.1002/art.20217. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Navarro-Sarabia F, Ariza-Ariza R, Hernandez-Cruz B, et al. Adalimumab for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;3:CD005113. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, et al. Predictors of joint damage in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis treated with high-dose methotrexate with or without concomitant infliximab: results from the ASPIRE trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:702–710. doi: 10.1002/art.21678. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

