A novel function of bamboo extract in relieving lipotoxicity
- PMID: 18350521
- PMCID: PMC4664535
- DOI: 10.1002/ptr.2395
A novel function of bamboo extract in relieving lipotoxicity
Abstract
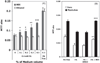
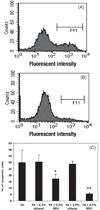
Lipotoxicity is closely related to the etiology and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. This study investigated the protective effect of an extract from bamboo Phyllostachys edulis against palmitic acid (PA)-induced lipoapoptosis. The lipo-detoxification function of the bamboo extract (BEX) was evaluated using cell culture models. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay and cell apoptosis was monitored by Annexin V staining. Cellular uptake of fluorescent free fatty acid (FFA) analog was measured by flow cytometry. Protein levels of total protein kinase B (Akt) and phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) were measured by western blotting. The results show that co-incubating BEX with mouse myoblast C2C12 cells had no effect on the cellular uptake of FFA, but dramatically decreased PA-induced cell apoptosis and protected cell viability. A similar antilipotoxicity effect of BEX was observed in other mammalian cells. BEX significantly decreased the protein levels of both Akt and p-Akt in C2C12 cells under normal cell culture conditions but not under lipotoxic conditions, indicating the regulatory effect of BEX on cell signaling pathways and its response to a high FFA environment. This study demonstrated a novel function of bamboo extract in preventing lipotoxicity in mammalian cells, implicating a promising phytotherapeutic approach for lipo-detoxification.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phyllostachys edulis compounds inhibit palmitic acid-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) production.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045082. Epub 2012 Sep 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028772 Free PMC article.
-
Bamboo extract reduces interleukin 6 (IL-6) overproduction under lipotoxic conditions through inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and AP-1 pathways.Cytokine. 2011 Jul;55(1):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.02.019. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Cytokine. 2011. PMID: 21474329 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitic acid-induced lipotoxicity promotes a novel interplay between Akt-mTOR, IRS-1, and FFAR1 signaling in pancreatic β-cells.Biol Res. 2019 Aug 19;52(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s40659-019-0253-4. Biol Res. 2019. PMID: 31426858 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of saturated palmitic acid and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on Sertoli cell apoptosis.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2018 Oct;64(5):368-380. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2018.1471554. Epub 2018 May 25. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2018. PMID: 29798686
-
Mangiferin Improved Palmitate-Induced-Insulin Resistance by Promoting Free Fatty Acid Metabolism in HepG2 and C2C12 Cells via PPARα: Mangiferin Improved Insulin Resistance.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Jan 27;2019:2052675. doi: 10.1155/2019/2052675. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 30809553 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Supplement of bamboo extract lowers serum monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 concentration in mice fed a diet containing a high level of saturated fat.Br J Nutr. 2011 Dec;106(12):1810-3. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511002157. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Br J Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21736779 Free PMC article.
-
Phyllostachys edulis compounds inhibit palmitic acid-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) production.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045082. Epub 2012 Sep 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028772 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Medicinal Application and Toxicity Evaluation of Extracts from Bamboo Plants.J Med Plant Res. 2015 Jun;9(23):681-692. doi: 10.5897/jmpr2014.5657. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Med Plant Res. 2015. PMID: 26617977 Free PMC article.
-
Bamboo extract reduces interleukin 6 (IL-6) overproduction under lipotoxic conditions through inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and AP-1 pathways.Cytokine. 2011 Jul;55(1):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.02.019. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Cytokine. 2011. PMID: 21474329 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of bamboo extract on hepatic biotransforming enzymes--findings from an obese-diabetic mouse model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Jan 7;133(1):37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.08.062. Epub 2010 Sep 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20832461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyle JP, Honeycutt AA, Narayan KM, et al. Projection of diabetes burden through 2050: impact of changing demography and disease prevalence in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1936–1940. - PubMed
-
- Cacicedo JM, Benjachareowong S, Chou E, Ruderman NB, Ido Y. Palmitate induced apoptosis in cultured bovine retinal pericytes: roles of NAD(P)H oxidase, oxidant stress, and ceramide. Diabetes. 2005;54:1838–1845. - PubMed
-
- de Vries JE, Vork MM, Roemen TH, et al. Saturated but not mono-unsaturated fatty acids induce apoptotic cell death in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. J Lipid Res. 1997;38:1384–1394. - PubMed
-
- Frustaci A, Kajstura J, Chimenti C, et al. Myocardial cell death in human diabetes. Circ Res. 2000;87:1123–1132. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, Hjortland M, Castelli WP. Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. Am J Cardiol. 1974;34:29–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

