A novel function of bamboo extract in relieving lipotoxicity
- PMID: 18350521
- PMCID: PMC4664535
- DOI: 10.1002/ptr.2395
A novel function of bamboo extract in relieving lipotoxicity
Abstract
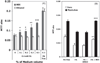
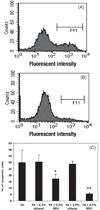
Lipotoxicity is closely related to the etiology and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. This study investigated the protective effect of an extract from bamboo Phyllostachys edulis against palmitic acid (PA)-induced lipoapoptosis. The lipo-detoxification function of the bamboo extract (BEX) was evaluated using cell culture models. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay and cell apoptosis was monitored by Annexin V staining. Cellular uptake of fluorescent free fatty acid (FFA) analog was measured by flow cytometry. Protein levels of total protein kinase B (Akt) and phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) were measured by western blotting. The results show that co-incubating BEX with mouse myoblast C2C12 cells had no effect on the cellular uptake of FFA, but dramatically decreased PA-induced cell apoptosis and protected cell viability. A similar antilipotoxicity effect of BEX was observed in other mammalian cells. BEX significantly decreased the protein levels of both Akt and p-Akt in C2C12 cells under normal cell culture conditions but not under lipotoxic conditions, indicating the regulatory effect of BEX on cell signaling pathways and its response to a high FFA environment. This study demonstrated a novel function of bamboo extract in preventing lipotoxicity in mammalian cells, implicating a promising phytotherapeutic approach for lipo-detoxification.
Figures


References
-
- Boyle JP, Honeycutt AA, Narayan KM, et al. Projection of diabetes burden through 2050: impact of changing demography and disease prevalence in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1936–1940. - PubMed
-
- Cacicedo JM, Benjachareowong S, Chou E, Ruderman NB, Ido Y. Palmitate induced apoptosis in cultured bovine retinal pericytes: roles of NAD(P)H oxidase, oxidant stress, and ceramide. Diabetes. 2005;54:1838–1845. - PubMed
-
- de Vries JE, Vork MM, Roemen TH, et al. Saturated but not mono-unsaturated fatty acids induce apoptotic cell death in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. J Lipid Res. 1997;38:1384–1394. - PubMed
-
- Frustaci A, Kajstura J, Chimenti C, et al. Myocardial cell death in human diabetes. Circ Res. 2000;87:1123–1132. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, Hjortland M, Castelli WP. Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. Am J Cardiol. 1974;34:29–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

