Virulizin induces production of IL-17E to enhance antitumor activity by recruitment of eosinophils into tumors
- PMID: 18351336
- PMCID: PMC11030271
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-008-0502-9
Virulizin induces production of IL-17E to enhance antitumor activity by recruitment of eosinophils into tumors
Abstract
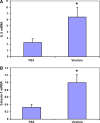
Virulizin has demonstrated strong antitumor efficacy in a variety of human tumor xenograft models including melanoma, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer and prostate cancer. Our previous studies have demonstrated that macrophages, NK cells, and cytokines are important in the antitumor mechanism of Virulizin. Virulizin treatment of tumor bearing mice results in the expansion as well as increased activity of monocytes/macrophages and production of cytokines IL-12 and TNFalpha and activation of NK cells. In this study we show that the inflammatory cytokine IL-17E (IL-25) is induced by Virulizin treatment and is part of its antitumor mechanism. IL-17E is a proinflammatory cytokine, which induces a T(H)2 type immune response, associated with eosinophil expansion and infiltration into mucosal tissues. IL-17E was increased in sera of Virulizin-treated mice bearing human melanoma xenografts, compared to saline-treated controls, as shown by 2D gel electrophoresis and ELISA. Treatment of splenocytes in vitro with Virulizin resulted in increased IL-17E mRNA expression, which peaked between 24 and 32 h post-stimulation. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that B cells produced IL-17E in response to Virulizin treatment. Furthermore, Virulizin treatment in vivo resulted in increased blood eosinophilia and eosinophil infiltration into tumors. Finally, injection of recombinant IL-17E showed antitumor activity towards xenografted tumors, which correlated with increased eosinophilia in blood and tumors. Taken together, these results support another antitumor mechanism mediated by Virulizin, through induction of IL-17E by B cells, leading to recruitment of eosinophils into tumors, which may function in parallel with macrophages and NK cells in mediating tumor destruction.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Virulizin, a novel immunotherapy agent, activates NK cells through induction of IL-12 expression in macrophages.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005 Nov;54(11):1115-26. doi: 10.1007/s00262-005-0698-x. Epub 2005 May 13. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005. PMID: 15891881 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17E, a proinflammatory cytokine, has antitumor efficacy against several tumor types in vivo.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010 Jun;59(6):805-17. doi: 10.1007/s00262-009-0802-8. Epub 2009 Dec 13. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010. PMID: 20012860 Free PMC article.
-
NK cell activation and tumor infiltration are involved in the antitumor mechanism of Virulizin.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005 Mar;54(3):229-42. doi: 10.1007/s00262-004-0582-0. Epub 2004 Sep 17. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005. PMID: 15378281 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-25: New perspective and state-of-the-art in cancer prognosis and treatment approaches.Cancer Med. 2021 Aug;10(15):5191-5202. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4060. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34128588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological activities and antitumor mechanism of an immunopotentiating organogermanium compound, Ge-132 (review).In Vivo. 1987 Jul-Aug;1(4):189-203. In Vivo. 1987. PMID: 2979786 Review.
Cited by
-
Nrf2 Induces IL-17D to Mediate Tumor and Virus Surveillance.Cell Rep. 2016 Aug 30;16(9):2348-58. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.075. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27545889 Free PMC article.
-
Immune analysis of expression of IL-17 relative ligands and their receptors in bladder cancer: comparison with polyp and cystitis.BMC Immunol. 2016 Oct 3;17(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12865-016-0174-8. BMC Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27716046 Free PMC article.
-
Th17 cells: positive or negative role in tumor?Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010 Jul;59(7):979-87. doi: 10.1007/s00262-010-0849-6. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010. PMID: 20352428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17-dependent, IFN-gamma-independent tumor rejection is mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and occurs at extraocular sites, but is excluded from the eye.J Immunol. 2011 Oct 15;187(8):4219-28. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100826. Epub 2011 Sep 14. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21918192 Free PMC article.
-
Differential dose effects of recombinant IL-25 on the development of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.Inflamm Res. 2010 Oct;59(10):879-87. doi: 10.1007/s00011-010-0200-x. Epub 2010 May 20. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 20490892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feng N, Jin H, Wang M, Du C, Wright JA, Young AH. Antitumor activity of Virulizin, a novel biological response modifier (BRM) in a panel of human pancreatic cancer and melanoma xenografts. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003;51:247–255. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Ferdinandi ES, Ely G, Joshi SS. Virulizin-2 gamma, a novel immunotherapeutic agent, in treatment of human pancreatic cancer xenografts. Int J Oncol. 2000;16:1015–1020. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

