Increased microerythrocyte count in homozygous alpha(+)-thalassaemia contributes to protection against severe malarial anaemia
- PMID: 18351796
- PMCID: PMC2267813
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050056
Increased microerythrocyte count in homozygous alpha(+)-thalassaemia contributes to protection against severe malarial anaemia
Abstract
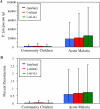
Background: The heritable haemoglobinopathy alpha(+)-thalassaemia is caused by the reduced synthesis of alpha-globin chains that form part of normal adult haemoglobin (Hb). Individuals homozygous for alpha(+)-thalassaemia have microcytosis and an increased erythrocyte count. Alpha(+)-thalassaemia homozygosity confers considerable protection against severe malaria, including severe malarial anaemia (SMA) (Hb concentration < 50 g/l), but does not influence parasite count. We tested the hypothesis that the erythrocyte indices associated with alpha(+)-thalassaemia homozygosity provide a haematological benefit during acute malaria.
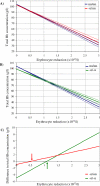
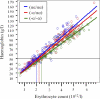
Methods and findings: Data from children living on the north coast of Papua New Guinea who had participated in a case-control study of the protection afforded by alpha(+)-thalassaemia against severe malaria were reanalysed to assess the genotype-specific reduction in erythrocyte count and Hb levels associated with acute malarial disease. We observed a reduction in median erythrocyte count of approximately 1.5 x 10(12)/l in all children with acute falciparum malaria relative to values in community children (p < 0.001). We developed a simple mathematical model of the linear relationship between Hb concentration and erythrocyte count. This model predicted that children homozygous for alpha(+)-thalassaemia lose less Hb than children of normal genotype for a reduction in erythrocyte count of >1.1 x 10(12)/l as a result of the reduced mean cell Hb in homozygous alpha(+)-thalassaemia. In addition, children homozygous for alpha(+)-thalassaemia require a 10% greater reduction in erythrocyte count than children of normal genotype (p = 0.02) for Hb concentration to fall to 50 g/l, the cutoff for SMA. We estimated that the haematological profile in children homozygous for alpha(+)-thalassaemia reduces the risk of SMA during acute malaria compared to children of normal genotype (relative risk 0.52; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.24-1.12, p = 0.09).
Conclusions: The increased erythrocyte count and microcytosis in children homozygous for alpha(+)-thalassaemia may contribute substantially to their protection against SMA. A lower concentration of Hb per erythrocyte and a larger population of erythrocytes may be a biologically advantageous strategy against the significant reduction in erythrocyte count that occurs during acute infection with the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. This haematological profile may reduce the risk of anaemia by other Plasmodium species, as well as other causes of anaemia. Other host polymorphisms that induce an increased erythrocyte count and microcytosis may confer a similar advantage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Weatherall DJ, Clegg JB. The Thalassaemia syndromes. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 2001.
-
- Ganczakowski M, Bowden DK, Maitland K, Williams TN, O'Shaughnessy D, et al. Thalassaemia in Vanuatu, south-west Pacific: frequency and haematological phenotypes of young children. Br J Haematol. 1995;89:485–495. - PubMed
-
- Williams TN, Maitland K, Ganczakowski M, Peto TE, Clegg JB, et al. Red blood cell phenotypes in the alpha+ thalassaemias from early childhood to maturity. Br J Haematol. 1996;95:266–272. - PubMed
-
- Haldane JBS. The rate of mutation of human genes. Proceedings of the 8th International Congress of Genetics. 1948;35:267–273. In:
-
- Flint J, Hill AV, Bowden DK, Oppenheimer SJ, Sill PR, et al. High frequencies of alpha-thalassaemia are the result of natural selection by malaria. Nature. 1986;321:744–750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

