Hydrogen peroxide mediates the radiation-induced mutator phenotype in mammalian cells
- PMID: 18352860
- PMCID: PMC2677991
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20071643
Hydrogen peroxide mediates the radiation-induced mutator phenotype in mammalian cells
Abstract
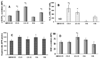
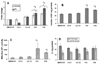
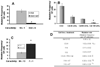
Chronic oxidative stress has been associated with genomic instability following exposure to ionizing radiation. However, results showing direct causal linkages between specific ROS (reactive oxygen species) and the ionizing radiation-induced mutator phenotype are lacking. The present study demonstrates that ionizing radiation-induced genomically unstable cells (characterized by chromosomal instability and an increase in mutation and gene amplification frequencies) show a 3-fold increase in steady-state levels of hydrogen peroxide, but not superoxide. Furthermore, stable clones isolated from parallel studies showed significant increases in catalase and GPx (glutathione peroxidase) activity. Treatment of unstable cells with PEG-CAT (polyethylene glycol-conjugated catalase) reduced the mutation frequency and mutation rate in a dose-dependent fashion. In addition, inhibiting catalase activity in the stable clones using AT (3-aminotriazole) increased mutation frequency and rate. These results clearly demonstrate the causal relationship between chronic oxidative stress mediated by hydrogen peroxide and the mutator phenotype that persists for many generations following exposure of mammalian cells to ionizing radiation.
Figures
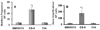
References
-
- Morgan WF. Non-targeted and delayed effects of exposure to ionizing radiation: II. radiation-induced genomic instability and bystander effects in vivo, clastogenic factors and transgenerational effects. Rad. Res. 2003;159:581–596. - PubMed
-
- Azzam EI, de Toledo SM, Spitz DR, Little JB. Oxidative metabolism modulates signal transduction and micronucleus formation in bystander cells from alpha-particle-irradiated normal human fibroblast cultures. Cancer Res. 2002;62:5436–5442. - PubMed
-
- Hunt CR, Sim JE, Sullivan SJ, Featherstone T, Golden W, Von Kapp-Herr C, Hock RA, Gomez RA, Parsian AJ, Spitz DR. Genomic instability and catalase gene amplification induced by chronic exposure to oxidative stress. Cancer Res. 1998;58:3986–3992. - PubMed
-
- Clutton SM, Townsend KM, Walker C, Ansell JD, Wright EG. Radiation-induced genomic instability and persisting oxidative stress in primary bone marrow cultures. Carcinogenesis. 1996;17:1633–1639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

