Acute myocardial infarction in young adults who abuse amphetamines
- PMID: 18353567
- PMCID: PMC2533107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2008.01.027
Acute myocardial infarction in young adults who abuse amphetamines
Abstract
Background: Case reports suggest a link between methamphetamine abuse and acute myocardial infarction (AMI), but no epidemiologic studies have examined this link. Our objective was to test the hypothesis that young adults who abuse amphetamines are at higher risk for AMI.
Methods: In this study of 3,148,165 discharges from Texas hospitals in a quality indicators database during 2000-2003, among persons aged 18-44 years we identified 11,011 AMIs, defined according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality's AMI mortality inpatient quality indicator.
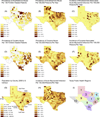
Results: In a multiple logistic regression analysis - while controlling for cocaine abuse, alcohol abuse, tobacco use, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, lipid disorders, obesity, congenital defects, and coagulation defects - amphetamine abuse was significantly associated with AMI (adjusted odds ratio=1.61; 95% CI=1.24-2.04, p=0.0004). The rate of AMIs among amphetamine abusers increased significantly from 2000 to 2003. The population attributable risk suggests that amphetamine abuse is responsible for 0.2% of AMIs in the state of Texas. The geographical distribution of amphetamine abuse varied by region, with the prevalence being highest in the North Texas and Panhandle regions of Texas.
Conclusions: This modest, though statistically robust, association suggests that amphetamine abuse may play a role in AMI.
Figures

References
-
- American Hospital Association. AHA guide to the health care field American Hospital Association. Chicago: 2004.
-
- Bashour TT. Acute myocardial infarction resulting from amphetamine abuse: a spasm-thrombus interplay? Am Heart J. 1994;128:1237–1239. - PubMed
-
- Basso C, Maron BJ, Corrado D, Thiene G. Clinical profile of congenital coronary artery anomalies with origin from the wrong aortic sinus leading to sudden death in young competitive athletes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:1493–1501. - PubMed
-
- Bateman BT, Schumacher HC, Bushnell CD, Pile-Spellman J, Simpson LL, Sacco RL, Berman MF. Intracerebral hemorrhage in pregnancy: frequency, risk factors, and outcome. Neurology. 2006;67:424–429. - PubMed
-
- Bruzzi P, Green SB, Byar DP, Brinton LA, Schairer C. Estimating the population attributable risk for multiple risk factors using case-control data. Am J Epidemiol. 1985;122:904–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

