Unilamellar vesicle formation and encapsulation by microfluidic jetting
- PMID: 18353990
- PMCID: PMC2290793
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0710875105
Unilamellar vesicle formation and encapsulation by microfluidic jetting
Abstract
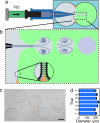
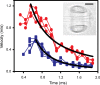
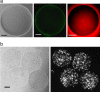
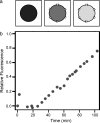
Compartmentalization of biomolecules within lipid membranes is a fundamental requirement of living systems and an essential feature of many pharmaceutical therapies. However, applications of membrane-enclosed solutions of proteins, DNA, and other biologically active compounds have been limited by the difficulty of forming unilamellar vesicles with controlled contents in a repeatable manner. Here, we demonstrate a method for simultaneously creating and loading giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) using a pulsed microfluidic jet. Akin to blowing a bubble, the microfluidic jet deforms a planar lipid bilayer into a vesicle that is filled with solution from the jet and separates from the planar bilayer. In contrast with existing techniques, our method rapidly generates multiple monodisperse, unilamellar vesicles containing solutions of unrestricted composition and molecular weight. Using the microfluidic jetting technique, we demonstrate repeatable encapsulation of 500-nm particles into GUVs and show that functional pore proteins can be incorporated into the vesicle membrane to mediate transport. The ability of microfluidic jetting to controllably encapsulate solutions inside of GUVs creates new opportunities for the study and use of compartmentalized biomolecular systems in science, industry, and medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid bilayer vesicle generation using microfluidic jetting.J Vis Exp. 2014 Feb 21;(84):e51510. doi: 10.3791/51510. J Vis Exp. 2014. PMID: 24637415 Free PMC article.
-
Mixing solutions in inkjet formed vesicles.Methods Enzymol. 2009;465:75-94. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)65004-7. Methods Enzymol. 2009. PMID: 19913162 Free PMC article.
-
On-chip generation of monodisperse giant unilamellar lipid vesicles containing quantum dots.Electrophoresis. 2016 May;37(10):1353-8. doi: 10.1002/elps.201600035. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Electrophoresis. 2016. PMID: 26920999
-
Synthesizing artificial cells from giant unilamellar vesicles: state-of-the art in the development of microfluidic technology.Bioessays. 2012 Nov;34(11):992-1001. doi: 10.1002/bies.201200105. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Bioessays. 2012. PMID: 22926929 Review.
-
Advances in giant unilamellar vesicle preparation techniques and applications.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023 Aug;318:102935. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2023.102935. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023. PMID: 37320960 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering protocells: prospects for self-assembly and nanoscale production-lines.Life (Basel). 2015 Mar 25;5(2):1019-53. doi: 10.3390/life5021019. Life (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25815781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NANOSCALE SELF-ASSEMBLY FOR DELIVERY OF THERAPEUTICS AND IMAGING AGENTS.Technol Innov. 2011 Jan 1;13(1):5-25. doi: 10.3727/194982411X13003853539948. Technol Innov. 2011. PMID: 24077873 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-aided biochemical programming of synthetic microreactors as diagnostic devices.Mol Syst Biol. 2018 Apr 26;14(4):e7845. doi: 10.15252/msb.20177845. Mol Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29700076 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic approaches for producing lipid-based nanoparticles for drug delivery applications.Biophys Rev (Melville). 2023 Sep 18;4(3):031304. doi: 10.1063/5.0150345. eCollection 2023 Sep. Biophys Rev (Melville). 2023. PMID: 38505779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Practical Guide to Preparation and Applications of Giant Unilamellar Vesicles Formed via Centrifugation of Water-in-Oil Emulsion Droplets.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;13(4):440. doi: 10.3390/membranes13040440. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37103867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sessa G, Weissman G. Incorporation of lysozyme into liposomes—A model for structure-linked latency. J Biol Chem. 1970;245:3295–3301. - PubMed
-
- Walde P. Enzymatic reactions in liposomes. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci. 1996;1:638–644.
-
- Lasic DD, Papahadjopoulos D. Liposomes revisited. Science. 1995;267:1275–1276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

